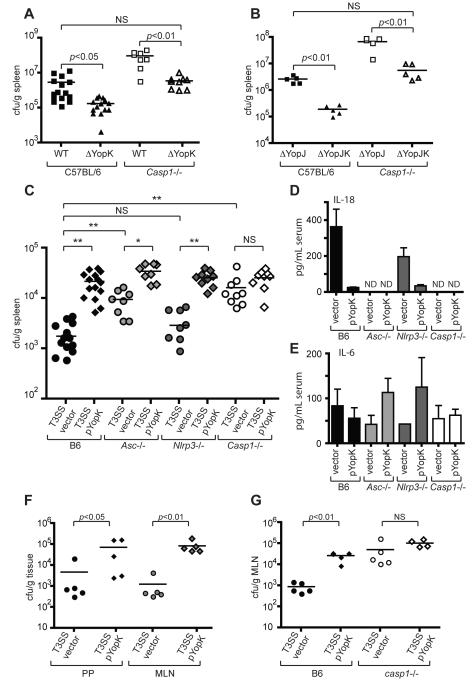
Figure 6. YopK inhibits caspase-1 dependent bacterial clearance in vivo.
(A) WT and Casp1-/- mice were infected intraperitoneally with WT or yopK mutant bacteria, or (B) yopJ or yopJK mutant bacteria, and spleen homogenates were plated 4 days post-infection to determine bacterial CFU per gram of tissue. (C) WT, Asc-/-, Nrlp3-/-, and Casp1-/- mice were infected as in (A) with either T3SS vector control or T3SS pYopK bacteria, and bacterial CFU per gram of tissue were determined. (D) Sera from mice in (C) were harvested and analyzed by ELISA for levels of circulating IL-18 or (E) IL-6. (F) WT mice were infected orally with indicated bacterial strains, and CFU per gram of Peyer’s patches and mesenteric lymph nodes was determined. (G) WT or Casp1-/- mice were infected as in (F) and bacterial load in mesenteric lymph nodes was determined. Statistical significance was analyzed by Student’s two-tailed t-test. * p<0.0002, ** p<0.0001. Data represent 2 to 3 independent pooled experiments (A, B, C) or at least three independent experiments for C57BL/6 mice and two independent experiments for knockout mice (F, G).