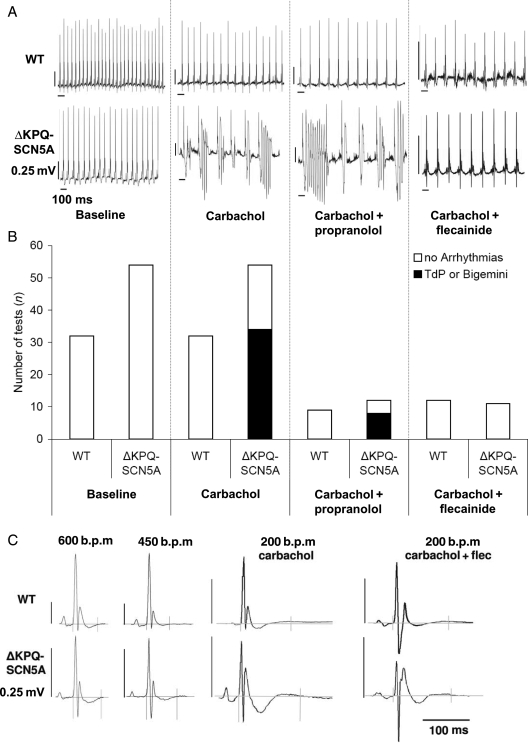
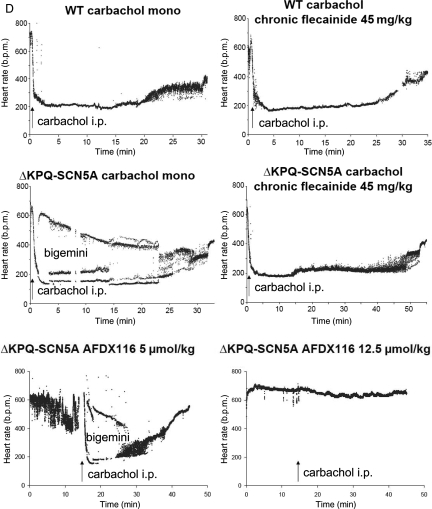
Figure 3.
Effect of carbachol on ECG morphology and arrhythmias in unrestrained ΔKPQ-SCN5A mice with and without chronic propranolol or flecainide treatment. (A) Representative telemetry ECG recordings at baseline and during carbachol challenge with and without chronic propranolol or flecainide treatment in unrestrained ΔKPQ-SCN5A mice. (B) Bar graphs give numbers of experiments with arrhythmias (filled bars, one to three challenges per animal) and without arrhythmias (open bars) in both genotypes. Carbachol induced arrhythmias in ΔKPQ-SCN5A mice only. Chronic flecainide prevented arrhythmias, chronic propranolol did not (all P < 0.05). (C) QT interval in unrestrained ΔKPQ-SCN5A and littermate WT mice. Tele-electrocardiographic summary potentials selected from spontaneous frequencies during heart rates at baseline (600 b.p.m, 450 b.p.m.), and low (200 b.p.m.) heart rates after carbachol challenge with or without chronic flecainide therapy. Carbachol-induced bradycardia exacerbated QT prolongation in ΔKPQ-SCN5A, (values and animal numbers in Table 2). (D) Telemetry heart rate during drug exposures. Alternating heart rate indicates bigemini and arrhythmias. Arrows indicate intraperitoneal injection of carbachol 0.5 mg/kg BW.