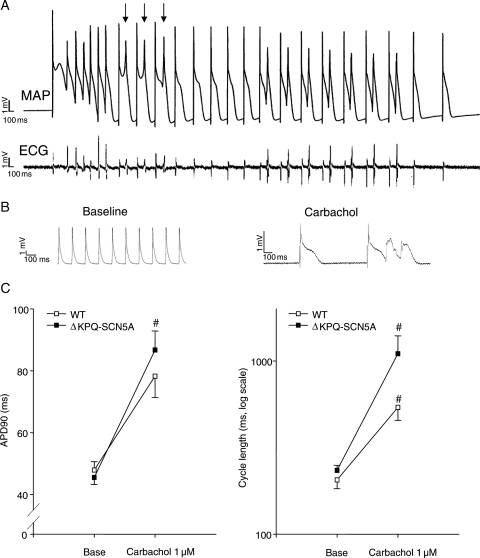
Figure 4.
Carbachol (10−7–10−5 M) provoked marked bradycardia, potential early afterdepolarizations (EADs), and ventricular arrhythmias in isolated, beating ΔKPQ-SCN5A mouse hearts. (A) Representative monophasic action potential recording of carbachol-induced TdP-like arrhythmias in an isolated, beating ΔKPQ-SCN5A mouse heart. Arrows indicate potentially conducted EADs. (B) Representative action potentials during spontaneous rhythm at baseline and after carbachol perfusion in a ΔKPQ-SCN5A mouse heart. (C) Mean action potential duration (left) and cycle length (right) during spontaneous rhythm in ΔKPQ-SCN5A and WT littermate mouse hearts. Carbachol provoked bradycardia and bradycardia-dependent APD prolongation in ΔKPQ-SCN5A mouse hearts (WT n = 24, ΔKPQ-SCN5A n = 28 hearts; P < 0.05 vs. WT and vs. baseline. Results depicted for carbachol 10−6 M; #P < 0.05 for carbachol vs. baseline).