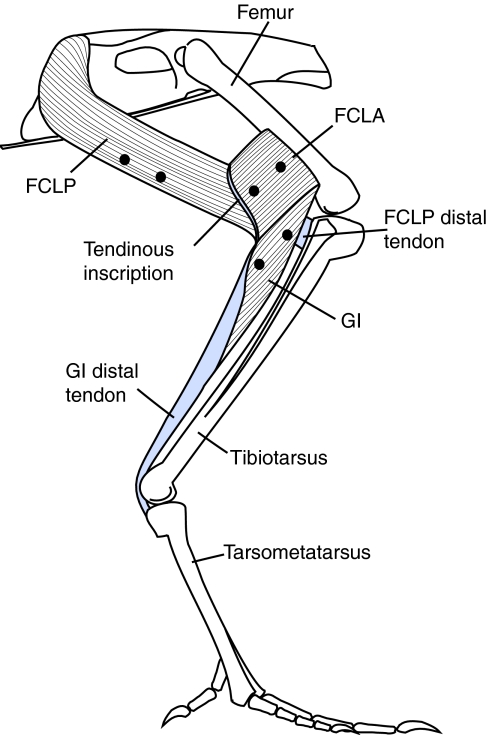
Fig. 1.
Lateral view of the flexor cruris lateralis pars pelvica (FCLP), flexor cruris lateralis pars accessoria (FCLA) and gastrocnemius intermedia (GI) muscles. The overlying musculature has been removed to expose the muscles, their origins and insertions. The flexor cruris medialis (FCM) (not shown) runs parallel and medial to the FCLP. Note that the orientation of the longitudinal axis of the fascicles does not necessarily represent the orientation in vivo when the muscles are active.