Figure 1.
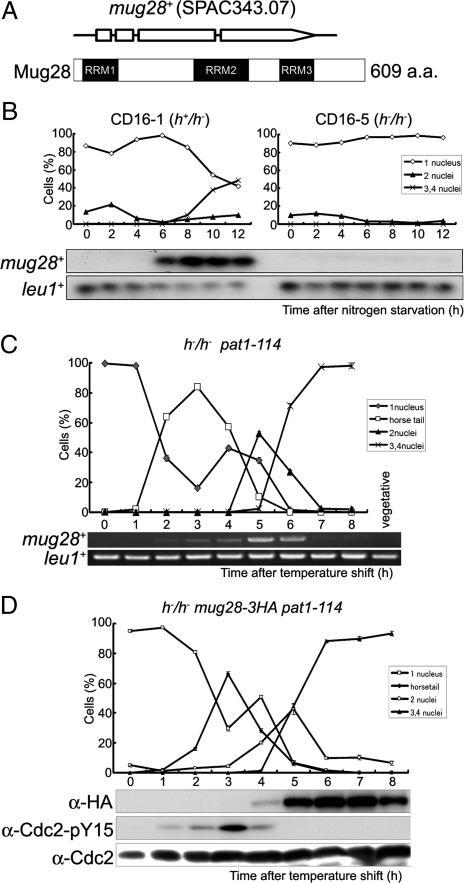
Mug28 is a meiosis-specific protein with three RRMs. (A) Schematic depictions of the Mug28 protein (609 amino acids) and the mug28+ gene, which consists of four exons (represented by three open boxes and an open arrow). The predicted RRMs were identified by SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) and are indicated by black boxes. (B) Northern blot analysis of mug28+ expression during meiosis. Total RNA was extracted from diploid h+/h− (CD16-1) and h−/h− (CD16-5) cells at the indicated times after the cells were subjected to nitrogen starvation, which induces CD16-1, but not CD16-5, cells to enter meiosis. The cells were collected at 2 h intervals and the total RNAs were blotted and probed with the mug28+ open reading frame (ORF) and leu1+ ORF (loading control). The graphs indicate the meiotic profiles of the cells used for RNA extraction. (C) RT-PCR analysis of mug28+ transcripts during meiosis. The h−/h− pat1-114 strain (JZ670) was induced to enter meiosis synchronously, and the total RNA was harvested, used for RT-PCR, and the PCR products were resolved by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. (D) Meiotic expression of Mug28-3HA. The h−/h− pat1-114 mug28+-3HA strain (AS122) was induced to enter meiosis synchronously by a temperature shift and the cells were collected at 1 h intervals for protein extraction, blotting, and probing with the anti-HA antibody. Phosphorylation of Cdc2-Y15 was also analyzed using an anti-Cdc2-Y15 antibody to help identify the meiotic stage at each time point. The Cdc2 levels were also examined, as a loading control. At each time point in B–D, the frequency of cells with one, two, three or four nuclei was determined by counting at least 200 Hoechst33342-stained cells under a microscope (top).