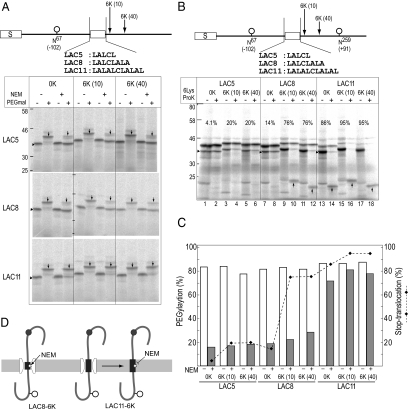
Figure 5.
LA8-segment spans membrane but exists in aqueous environment. (A) To assess water environment of H-segment, a single Cys residue, one glycosylation site (N67), and the 6K-cluster were included at the indicated positions of the Cys-less model protein. After translation in the presence of RM, an aliquot was incubated with NEM under native conditions, where SH-group in an aqueous environment reacts with NEM, and then treated with PEGmal under SDS-denaturing conditions. Only the SH-group integrated in membrane lipid is PEGylated. PEGylated products (↓) and monoglycosylated forms (▶) are indicated. (B) To assess stop-translocation efficiency of the LAC-segments, glycosylation sites were incorporated in the indicated positions. Monoglycosylated products (▶) and the ProK-resistant fragments (↑) are indicated. Stop-translocation percentages are indicated (%). (C) Quantification of PEGylation (%; □, NEM −;  , NEM +) and stop-translocation percent (%; ♦). (D) The LAC8-segment spanned the membrane depending on the 6K-cluster, but the Cys residue (☆) remained in a water-accessible environment, where the SH-group reacted with NEM and thus did not react with PEGmal. In contrast, the LAC11-segment was in a hydrophobic membrane environment, where the Cys residue did not react with NEM and thus reacted with PEGmal reagent.
, NEM +) and stop-translocation percent (%; ♦). (D) The LAC8-segment spanned the membrane depending on the 6K-cluster, but the Cys residue (☆) remained in a water-accessible environment, where the SH-group reacted with NEM and thus did not react with PEGmal. In contrast, the LAC11-segment was in a hydrophobic membrane environment, where the Cys residue did not react with NEM and thus reacted with PEGmal reagent.