Figure 3.
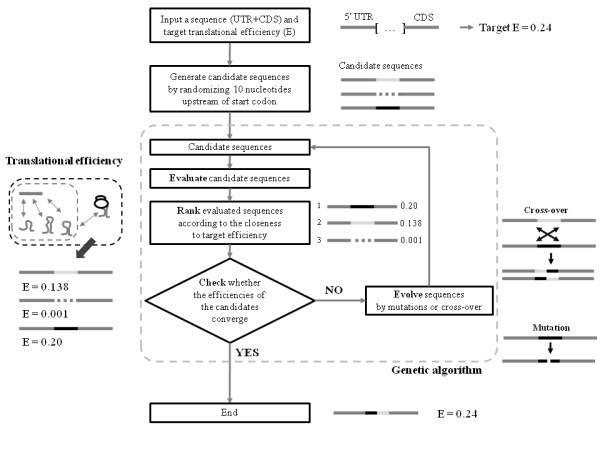
The use of a genetic algorithm to design synthetic RDS sequences having specific translational efficiencies. The RDS design process starts with a user-specified 5' untranslated region (UTR) and a coding sequence (CDS). The 10 nucleotides upstream of the start codon, which make up part of the RDS, are modified to satisfy a target translational efficiency using a genetic algorithm. The generated sequences are randomly mutated or crossed over. If the translational efficiency of the generated sequences converges to the target efficiency, the algorithm terminates.
