Fig. 4.
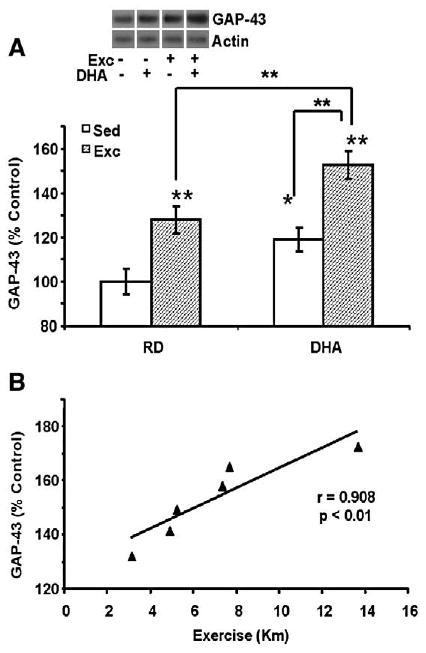
(A) The separate applications of exercise or the DHA diet elevated levels of GAP-43 while the concurrent application of both elevated GPA-43 levels further. Each value represents the mean latency±SEM (two-way ANOVA, *p<0.05, **p<0.01). (B) Levels of GAP-43 changed in proportion to the total amount of exercise in animals receiving DHA diet and exercise combined treatment (r=0.908, p<0.01).
