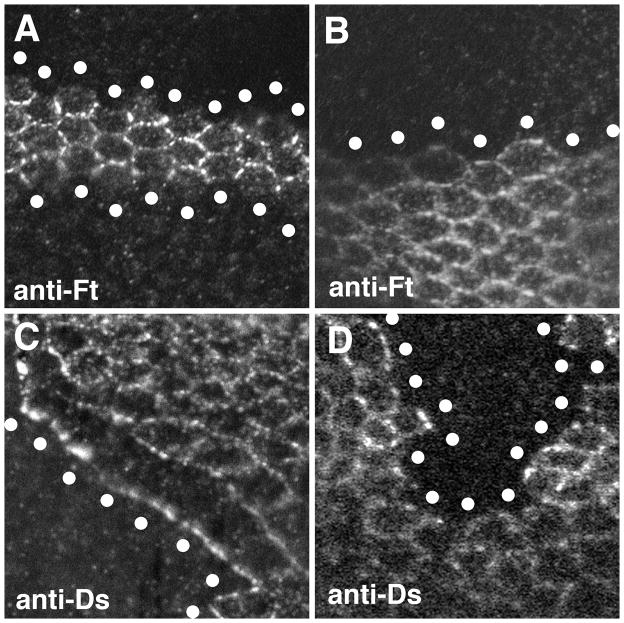
Figure 2. Effect of Fj on Fat-Ds localization.
Confocal images of pupal wing discs stained with either anti-Fat or anti-Ds as indicated. In each panel, the approximate center of the mutant cells at the edge of the clone are indicated by the white circles. The images are oriented with distal towards the right. A) Two clones of fat cells over-expressing Fj. Fat in the wild-type cells immediately adjacent to the Fj over-expressing cells fails to accumulate along the border with the Fj over-expressing cells. B) A clone of fat cells that do not overexpress Fj. In the absence of Fj over-expression, Fat is still present at the clone border. C) A clone of ds cells over-expressing Fj. Note that Ds in the adjacent wild-type cells is preferentially drawn to the border of the Fj over-expressing cells. This can be seen by the reduced Ds staining at the cell-cell boundaries between the wild-type cells that border the Fj over-expressing cells. D) A clone of ds cells that do not over-express Fj. No effect on Ds localization is seen in the adjacent wild-type cells. Similar effects on Fat and Ds localization can be observed on all sides of Fj over-expressing clones. The genotypes are A) hsFLP/+; TubGal80, FRT40A/ftG-rv, FRT40A; Tub-Gal4/UAS-Fj, B) hsFLP/+; P[Ubi-GFP]2L, FRT40A/ftG-rv, FRT40A, C) hsFLP/+; TubGal80, FRT40A/ds38k, FRT40A; Tub-Gal4/UAS-Fj and D) hsFLP/+; P[Ubi-GFP]2L, FRT40A/ds38k, FRT40A.