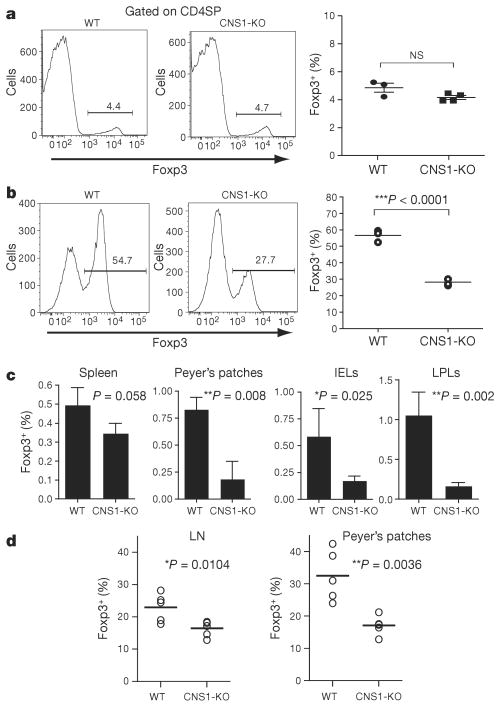
Figure 3. CNS1 controls peripheral, but not thymic, induction of Foxp3 expression.
a, Frequency of Foxp3+ Treg cells among thymic CD4SP cells in CNS1-KO mice or littermate controls. NS, not significant. b, Frequency of Foxp3+ iTreg cells generated after stimulation of TN cells from CNS1-KO or littermate control mice with anti-CD3 (1 μg ml−1), TGF-β (2 ng ml−1) and Ly5.1+ irradiated (20 Gy) T-cell-depleted splenocytes for 72h. c, Frequency of in vivo generated Foxp3+ iTreg cells among CD4+ cells in spleen, Peyer's patches, intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs), and lamina propria lymphocytes (LPLs). CNS1-KO or wild-type Ly5.2+CD4+Foxp3− naive T cells were co-transferred with wild-type Ly5.1+Foxp3+ Treg cells into T-cell-deficient recipient mice. Ten weeks later, Ly5.2+Foxp3+ cell populations were analysed by flow cytometry. Error bars denote mean ± s.d. d, Frequency of Foxp3+ Treg cells among CD4+ T cells in peripheral lymph nodes (LN; ‘non-mesenteric’), and Peyer's patches of 8–11-month-old CNS1-KO or littermate control mice.