Figure 5.
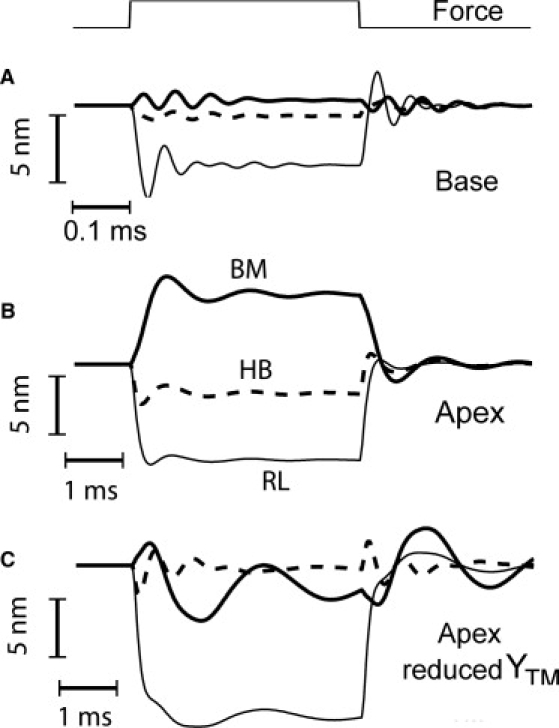
Dynamic responses of the organ of Corti to current injection. OHCs stimulated to produce an axial contractile force (fOHC) of 1 nN peak value distributed longitudinally with standard deviation σz = 60 μm at the base (A) and apex (B and C). (A) Base: time course of dynamic displacements of the basilar membrane (BM, thick line), hair bundle (HB, dashed line), and reticular lamina (RL, thin line) for a force-step timing that is shown in the top trace. (B) Apex: time courses of displacements for the same force step. (C) Apex: effects of a 1000-fold reduction in tectorial membrane attachment stiffness. In panel C, the hair bundle shows damped oscillations at a frequency (1.4 kHz) higher than the basilar membrane, determined by tectorial membrane mass and hair bundle stiffness. In the standard conditions, the basilar membrane displays damped oscillations at 0.7 kHz (apex) and 16 kHz (base).
