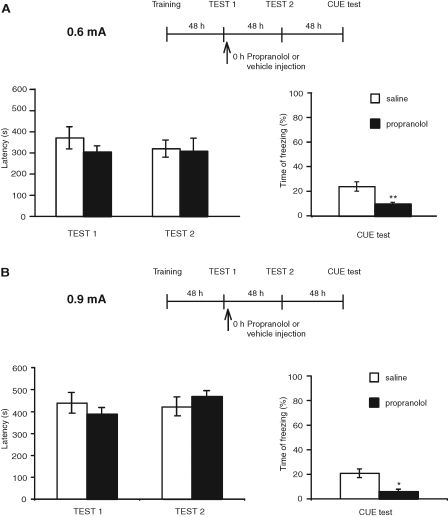
Figure 3.
Propranolol disrupts freezing but not IA memory. Experimental timelines are shown above each experiment. Values of latencies are expressed in seconds and shown as means ± SEM. Freezing scores are expressed as percent of the total time of testing and shown as means ± SEM. (A) Rats were trained in IA with 0.6 mA footshock intensity and, during training, presented with a tone. Forty-eight hours later, they were tested in IA, and immediately after, received an i.p. injection of propranolol or saline. Forty-eight hours and 96 h later, the animals were tested in IA and cue fear memory, respectively. Compared with saline, propranolol had no effect on IA retention, but significantly disrupted freezing (Student's t-test, [**] P < 0.01). (B) Rats underwent the same protocol as in A, except that a footshock of 0.9 mA was used during training. Compared with saline, propranolol had no effect on IA retention, but significantly disrupted freezing (Student's t-test, [*] P < 0.05).