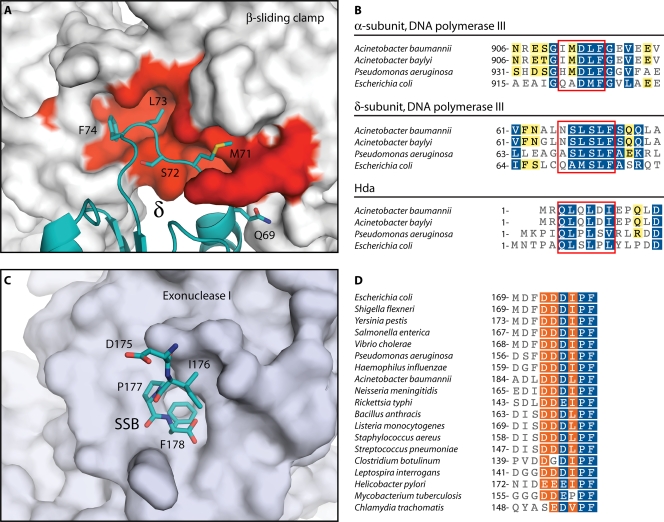
FIG. 3.
Highly conserved protein interaction modules in the Acinetobacter replisome. (A) Structure of the E. coli βδ complex (127). The solvent-accessible surface of β is shown in gray and red. Red indicates residues that are conserved in A. baylyi. The δ subunit is colored teal, and side chains are shown for the β-binding consensus residues. (B) Portions of sequence alignments for DNA replication proteins containing β-binding motifs. Boxes indicate β-binding motifs. Residues are highlighted as in Fig. 2. (C) Structure of E. coli exonuclease I bound to the C-terminal peptide of SSB (162). The solvent-accessible surface of exonuclease I is shown in gray. The C-terminal peptide of SSB is shown in teal. (D) Portion of a sequence alignment for SSB proteins. In panels B and D, white characters with blue shading indicate positions with homology across all sequences, white characters with orange shading indicate residues conserved in 80% of sequences, and black characters with yellow shading indicate 60% conservation. Sequence alignments were produced using the MUSCLE algorithm (72) within the Geneious software package (Biomatters). (Panels A and C were produced with PyMOL [64] using data from Protein Data Bank entries IJQL [127] and 3C94 [162], respectively.)