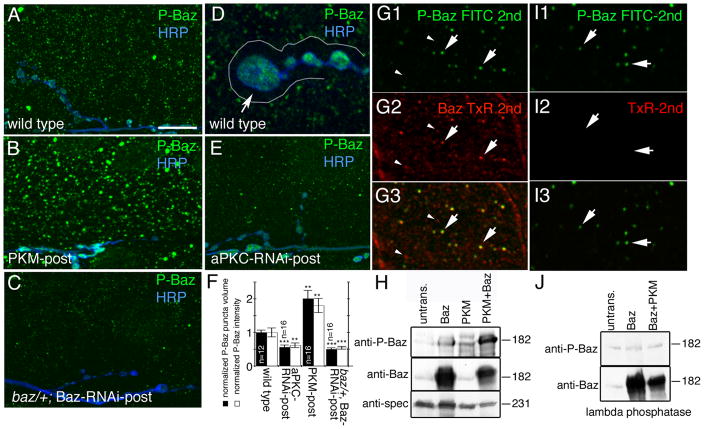
Figure 4. Baz is phosphorylated by aPKC in muscles and is absent from the postsynaptic F-actin-rich area.
(A–E) Third instar muscle regions and NMJs at muscles 6 or 7 in preparations labeled with anti-phospho Baz (green) and anti-HRP (blue) in (A, D) wild type, (B) PKM-post, (C) baz/+; Baz-RNAi-post and (E) aPKC-RNAi-post. Arrow in D points to the postsynaptic F-actin rich area outlined by a white line, which is devoid of phospho-Baz.
(F) Quantification of the volume and intensity of phospho-Baz puncta in muscles of wild type, aPKC-RNAi-post, and PKM-post. Data was normalized to wild type values (n represents number of muscles).
(G, I) Confocal image of a muscle region in a preparation (G) sequentially labeled with antibodies to P-Baz (green) and Baz (red) showing that each P-Baz puncta colocalizes to a Baz puncta (arrows), and that only a subset of Baz puncta contains phosphorylated P-Baz (arrowheads point to Baz puncta devoid of P-Baz immunoreactivity), and (I) treated similar to G, but in an experiment were the anti-Baz antibody was omitted to ensure that the first secondary antibody (FITC 2nd) saturated all anti-P-Baz sites, which is observed in I2 by the lack of signal upon incubation with the TxR-2nd antibody.
(H, J) Western blots of S2 cell extracts transfected with the constructs indicated above the blots and probed sequentially with the antibodies indicated at the left, showing (H) the phosphorylation of Baz by PKM and (J) the lambda phosphatase assay. Untrans=untransfected cells.
Calibration bar is 14 μm for A, B, C, E, 5 μm for D, and 2 μm for G.