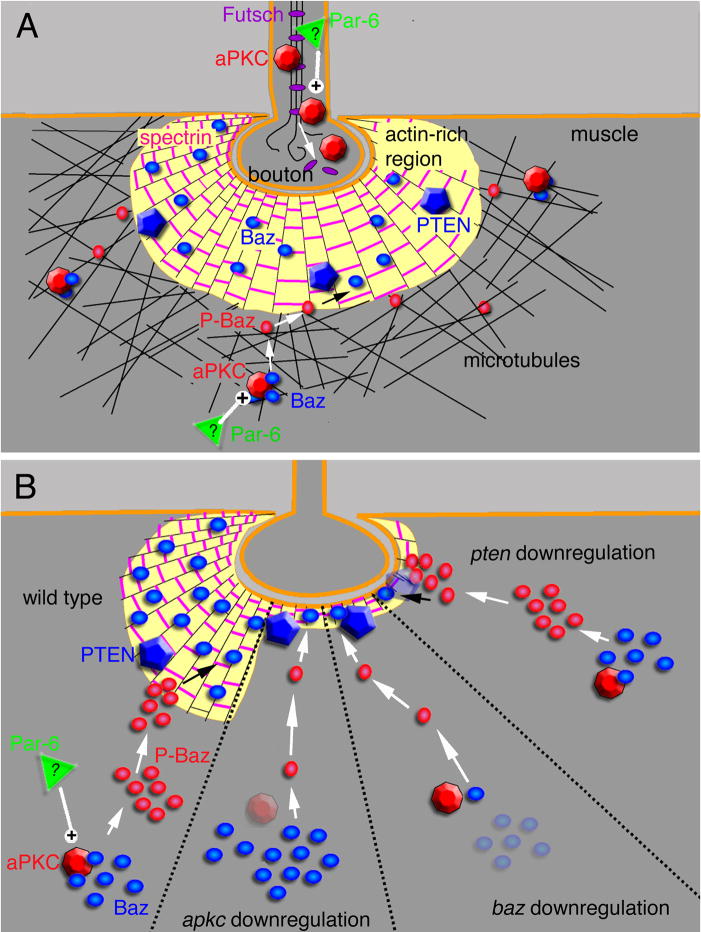
Figure 9. Proposed model for the regulation of the synaptic cytoskeleton by the aPKC-Baz-Par-6 complex at the larval NMJ.
(A) At the presynaptic compartment, aPKC regulates microtubule stability by facilitating an interaction between the MAP1B-related Futsch and bundled microtubules (see (Ruiz-Canada et al., 2004)). At the postsynaptic compartment, aPKC regulates both F-actin and microtubules (Ruiz-Canada et al., 2004). Here we propose that the regulation of the F-actin cytoskeleton is carried out through the opposing functions of aPKC and PTEN by modulating the phosphorylation state of Baz (see text for details).
In (B) the synaptic bouton has been subdivided into 4 regions, each representing a different genotype as indicated, and the consequence of each genotype on the F-actin-rich postsynaptic region (see text for details).