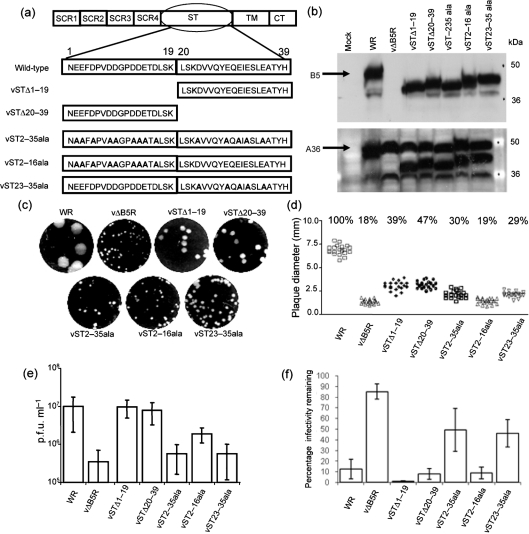
Fig. 3.
Mutational analysis of the B5 ST. (a) Mutations incorporated into the B5 ST (amino acids 1–39). (b) Immunoblot of the B5 and A36 proteins from infected cell lysates. BHK-21 cells were infected at 3 p.f.u. per cell and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. The cells were lysed and the proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (12 % gel). (Top) The membrane was probed with anti-B5 mAb 19C2. WT B5 (arrow) is 42 kDa. (Bottom) The membrane was then reprobed with anti-A36 mAb. A36 is approximately 50 kDa (arrow). (c) Plaque phenotype. BS-C-1 cell monolayers were infected and overlaid with DMEM/2.5 % FBS/1.5 % CMC. After a 10 day incubation period at 37 °C, cell monolayers were stained with crystal violet and scanned using a GelDoc imager. (d) Plaque size comparison. The diameter of 20 plaques of each virus from two independent experiments in (c) was measured and the percentage plaque size compared with that of WT WR plaques was calculated. (e) EEV titres: BHK-21 cells were infected at 3 p.f.u. per cell for 24 h and the supernatant was harvested, incubated with mAb 2D5 (diluted 1 : 2000) for 1 h at 37 °C and the infectivity was measured by plaque assay. Data shown are the mean±sd of at least three experiments. (f) Effect of HP on EEV membrane disruption, as in Fig. 2(b).