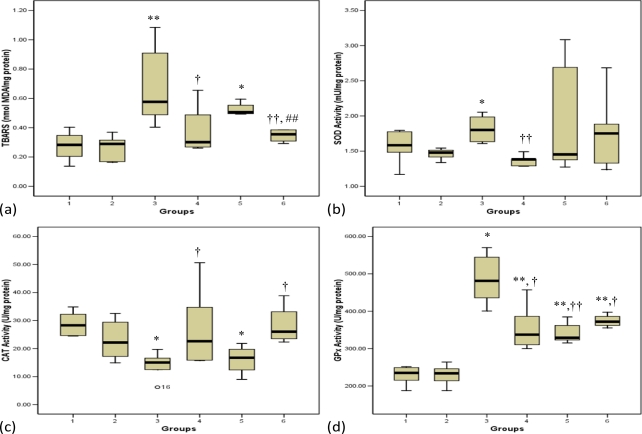
Figure 1.
Effects of honey, glibenclamide and metformin as well as their combination on (a) concentrations of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), (b) activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), (c) activity of catalase (CAT) and (d) activity of glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in pancreas of control and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Group 1 (Normal control); Group 2 (Normal + Honey); Group 3 (Diabetic control); Group 4 (Diabetic + Honey); Group 5 (Diabetic + Glibenclamide + Metformin); Group 6 (Diabetic + Glibenclamide + Metformin + Honey).
Each group consisted of five to seven animals. Data are expressed as median (interquartile range).
Values are statistically significant at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with group 1; †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 compared with group 3 and ## p< 0.01 compared with group 5.
One unit of SOD was defined as the amount of enzyme needed to exhibit 50% dismutation of superoxide radical.
One unit of CAT was defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of 1 μmol of H2O2 per minute.
One unit of GPx was defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of 1 nmol of NADPH per minute.