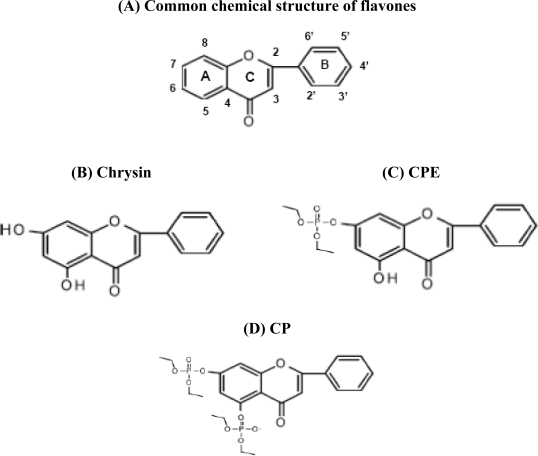
Figure 1.
(A) Common chemical structure of flavones. Flavones have a common chemical structure consisting of fused A and C rings, and a phenyl B ring attached to position 2 of the C ring. (B) Chrysin is in the flavone subgroup of flavonoids and shares a common flavone structure with hydroxyls at position 5 and 7 of the A ring. Replacing the hydroxyl with a phosphate group at position 7, such as in diethyl chrysin-7-yl phosphate (CPE). (C) or at positions 5 and 7, such as in tetraethyl bis-phosphoric ester of chrysin (CP). (D), enhances the anti-cancer potential of the chrysin.