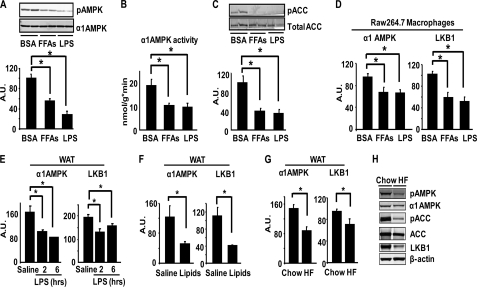
FIGURE 2.
AMPK signaling and expression in macrophages and adipose tissue are down-regulated by LPS, FFAs, HF diets, and lipid infusion. A–C, LPS and FFAs inhibit AMPK phosphorylation (A), activity (B), and ACC phosphorylation (C) in macrophages. Bone marrow macrophages were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) or FFAs (palmitate, oleate, and stearate mixture, 500 μm) for 2 h. D, LPS and FFAs inhibit the expression of α1AMPK and LKB1 in macrophages. RAW264.7 macrophages were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) or FFAs (250 μm) overnight. n = 6/group. E, LPS inhibits the mRNA expression of α1AMPK and LKB1 in epididymal WAT of mice. C57/BL6J mice (male, n = 4/group) were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (2 mg/kg body weight) and WAT were dissected 2 or 6 h after injection. F, increasing circulating FFAs inhibits the mRNA expression of α1AMPK and LKB1 in epididymal WAT in mice (n = 5/group). Mice were infused with lipids (5 ml/kg·h, liposyn II; coupled with 6 units/h of heparin) for 8 h. G and H, HF feeding inhibits the mRNA expression of α1AMPK and LKB1 (G) and AMPK signaling (H) in epididymal WAT of mice (n = 8/group). For A, C, and H, AMPK signaling was measured by immunoblotting. For B, α1AMPK activity was measured using an immunocomplex assay with SAMS peptide. For D–G, mRNA levels of target genes were measured by real time RT-PCR and normalized to cyclophilin. All data are expressed as mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05. A.U., arbitrary units.