FIGURE 5.
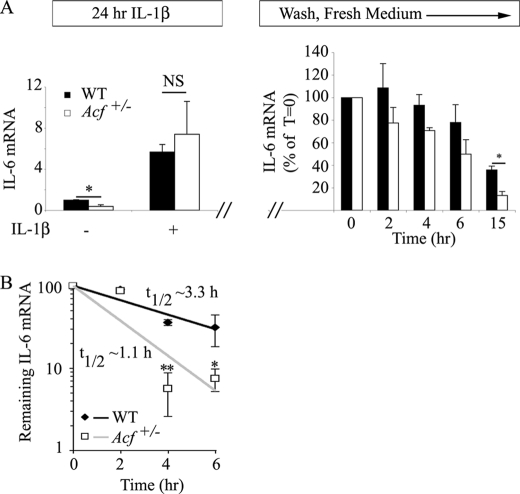
ACF stabilizes IL-6 mRNA. A, IL-6 mRNA steady state in MEFs. WT and Acf+/− MEFs were incubated in the presence of 1 ng/ml of IL-1β for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated from two independent preparations of MEFs. Baseline IL-6 mRNA was significantly (*, p = 0.018) lower in MEFs from Acf+/− mice, but both genotypes responded to IL-1β administration with a 5.7–7.4-fold increase in IL-6 mRNA in WT and Acf+/− mice, respectively. In a separate series of studies, following 1 ng/ml of IL-1β incubation for 24 h, MEFs were subjected to 2 washes with PBS, subsequently maintained in normal growth medium, and total RNA isolated at the indicated time points. IL-6 mRNA levels were determined by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR and normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Data represent mean ± S.E. from 4 independent assays per genotype (*, p = 0.033). B, KCs were isolated from WT and Acf+/− mice and plated at 4 × 105 cells per well in a 12-well plate. Following an overnight culture at 37 °C, medium was changed and supplemented with LPS (final concentration 500 ng/ml) for 1 h. Conditioned medium was collected, fresh medium containing actinomycin D (Act D) (10 μg/ml) was added, and RNA was harvested at the indicated time points. IL-6 mRNA levels were determined by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR and normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA. The t½ of IL-6 mRNA was 1.1 ± 0.14 h in Acf+/− KCs versus 3.3 ± 0.44 h in WT KCs. Data represent the mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments per genotype. Each experiment was performed with KCs isolated from three to four mice. *, p = 0.033; **, p = 0.0069.