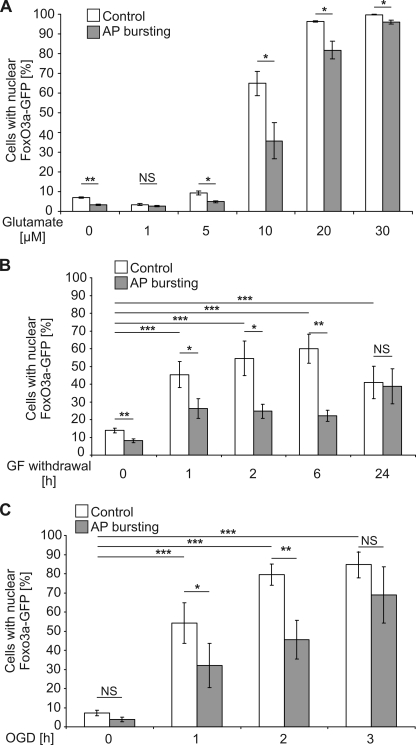
FIGURE 3.
Synaptic activity inhibits nuclear translocation of FoxO3a-GFP induced by cell death-promoting stimuli. Shown is a quantitative analysis of the percentage of hippocampal neurons with nuclear localized FoxO3a-GFP in cultures without exposure to a cell death-promoting stimulus or in cultures after stimulation for 1 h with the indicated glutamate concentrations (A), withdrawal of growth factors (GF) for the indicated times (B), or OGD for the indicated times (C). Before application of cell death-inducing stimuli, hippocampal neurons were treated for 16 h with 50 μm bicuculline to induce AP bursting or received no pretreatment (Control). Numbers of cells analyzed per condition (i.e. with and without cell death-inducing stimuli and with and without AP bursting): 9870, glutamate (n = 3); 12638, growth factor withdrawal (n = 6); 7941, OGD (n = 4). Statistically significant differences (ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test) are indicated with asterisks; ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. NS, not significant. Bars represent the means ± S.E. (n = 5).