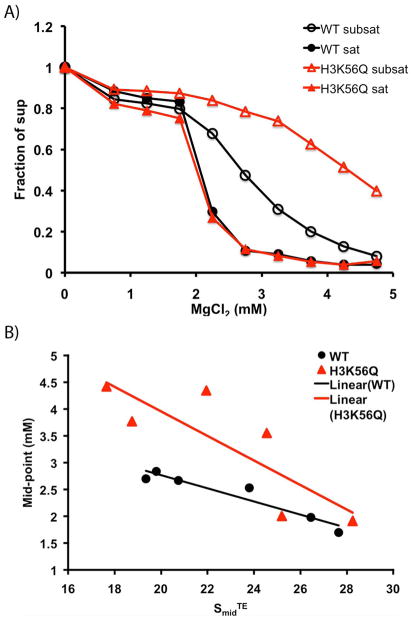
Figure 3. H3K56Q disrupts intermolecular oligomerization of subsaturated nucleosomal arrays.
A) Intermolecular oligomerization assay. Nucleosomal arrays were incubated with varying concentrations of MgCl2, followed by centrifugation. The fraction of array remaining in the supernatant is plotted as a function of MgCl2 concentration. Samples of the following saturation levels, indicated by SmidTE were analyzed: black circles, filled: wild type, 26.5S; black circles, open: wild type 20.8S; red triangles, filled: H3K56, 25.2S; red triangles, open: H3K56Q, 22S. B) Effect of nucleosomal array saturation on intermolecular oligomerization. Nucleosomal arrays were reconstituted at various ratios of histone octamer to 208 bp 5S DNA repeats. Arrays were analyzed by sedimentation velocity analysis in TE buffer to determine their degree of saturation (SmidTE). MgCl2 concentration required for half of the arrays to remain in the supernatant is plotted as a function of SmidTE. Black circles, wild type; red triangles, H3K56Q. Lines represent a linear regression through the data points.