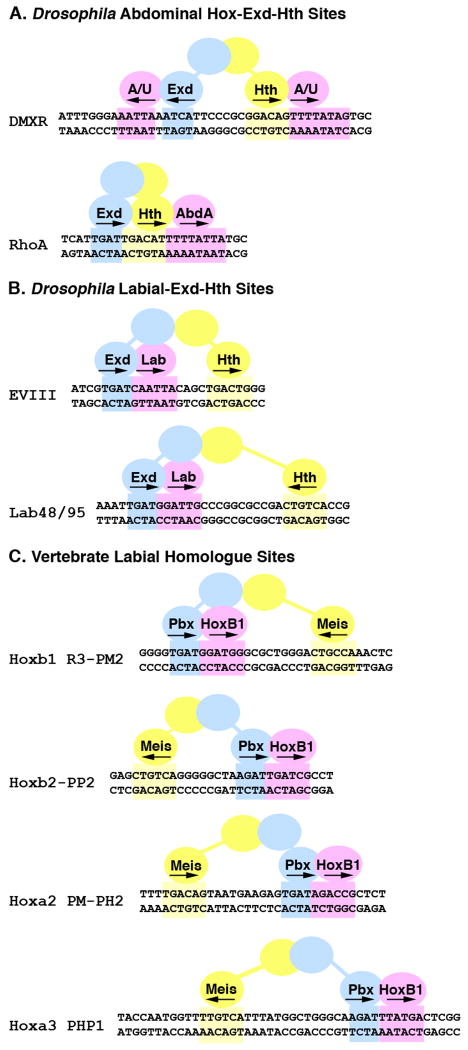
Figure 1. Configurations of Hox, Exd, and Hth binding sites in Drosophila and vertebrate cis-regulatory elements.
Schematics of eight Hox regulated enhancer elements with the Exd (blue), Hth (yellow) and Hox (pink) sites highlighted. A. Abdominal Hox target elements from Drosophila. The DMXR element contains both Exd/Hox and Hth/Hox sites that are bound by the Abd-A and Ubx (A/U) Hox factors to repress Dll expression in the abdomen (Gebelein et al., 2004). The RhoA element contains consecutive Exd/Hth/Hox binding sites that are bound by Abd-A to activate rhomboid expression in developing abdominal sensory cells (Li-Kroeger et al., 2008). B. The EVIII and Lab 48/95 elements are both activated by the Lab Hox factor in the developing gut endoderm and each contains a Hox, Exd, and Hth binding site (Ebner et al., 2005; Ryoo et al., 1999). C. Four mouse cis-regulatory elements containing Pbx/Hox and distant Meis binding sites. All are activated by the HoxB1 vertebrate homologue of Lab in collaboration with the Pbx and Meis proteins within the developing hindbrain (Ferretti et al., 2005; Ferretti et al., 2000; Manzanares et al., 2001; Popperl et al., 1995; Tumpel et al., 2007).