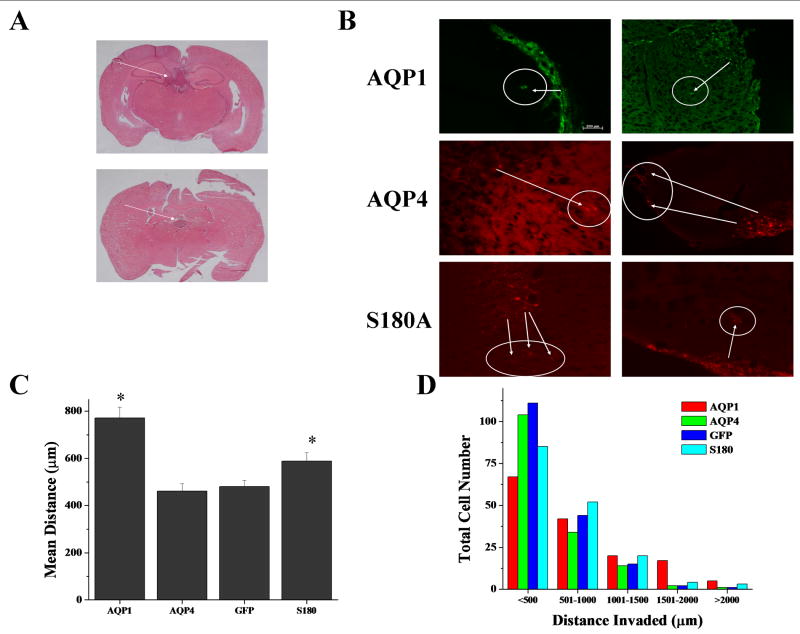
Figure 6.
AQP1 expression enhances tumor invasion. AQP1 (n=9), AQP4 (n=8) and S180A-AQP4 (n=8) expressing D54MG were injected intracranially into 6 weeks old mice. Representative images of tumor growth (A). Arrows indicate location of main tumor mass. Fluorescent images demonstrate tumor cell invasion away from the major tumor mass for D54 glioma cells expressing AQP1-GFP, AQP4-DsRed, or AQP4-S180A-DsRed (B). Arrows indicate invading cells. D54 cells expressing AQP1-GFP invaded ∼2 fold over D54-GFP and AQP4-DsRed expressing D54 cells (C). We measured invasion over 500 μm increments and discovered that AQP1 tumors were able to invade greater distances than either D54 or AQP4 cells (D). There were significantly more cells that had migrated distances greater than 1500 μm. Most D54 and AQP4 tumors invaded short distances, while S180A-AQP4 mutants invaded intermediate distances.