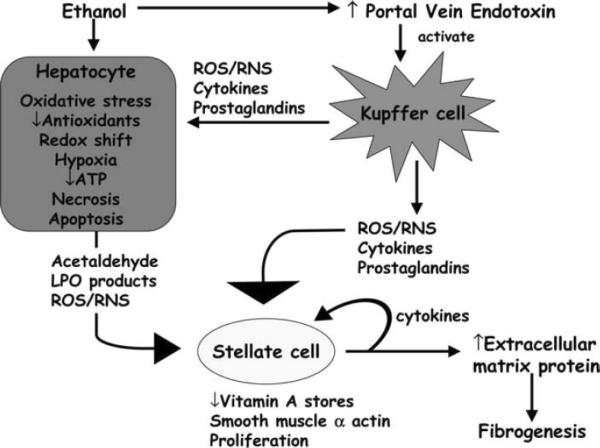
Figure 6.
Mechanism of alcohol-induced liver injury. Alcohol metabolism causes acetaldehyde and reactive oxygen species to be generated, both of which can activate stellate cells. ROS/RNS from Kupffer cells can also active stellate cells causing increasing collagen deposition and eventual fibrosis. Reprinted by permission from Halliwell B, JMC G. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. 4th ed. oxford: Oxford University Press; 2007. [59]