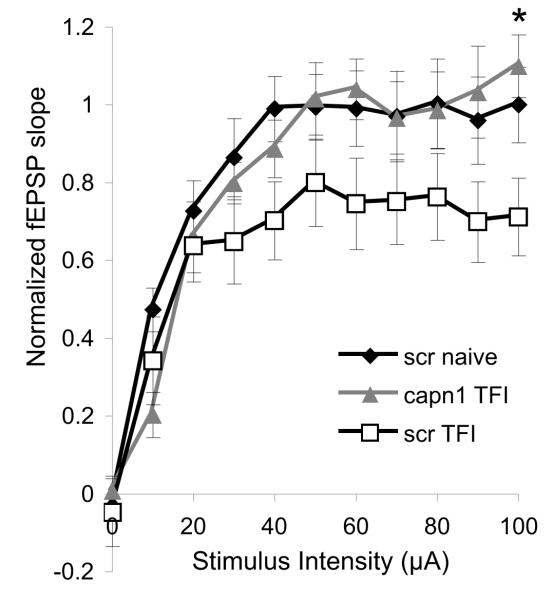
Figure 6.
Electrophysiologic function of post-ischemic CA1 pyramidal neurons protected by calpain 1 knockdown. Stimulus-response curves from hippocampal uninjured slices transduced with scrambled (scr, n = 9 slices from 3 animals) and injured slices transduced with scr (n = 9 slices from 3 animals) or calpain 1 (capn1, n = 8 slices from 3 animals) shRNA. The Schaffer collateral pathway was sequentially stimulated at increasing intensity and field excitatory post-synaptic potentials (fEPSPs) were recorded from CA1. An approximately 20% reduction in maximum fEPSP slope was observed in injured scr transduced slices compared to uninjured controls. This deficit was restored by transduction with capn1 shRNA. The fEPSP slope at the maximum stimulus intensity was significantly greater in injured capn1 transduced slices compared to injured scr transduced slices (p < 0.05, One-way ANOVA with Scheffe post-hoc analysis).