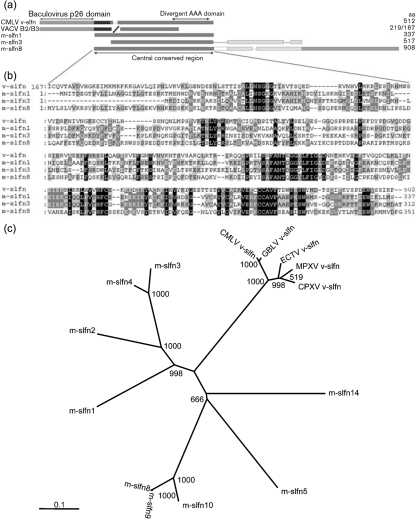
Fig. 1.
CMLV v-slfn is related to members of the mammalian slfn family. (a) Diagrammatic representation of CMLV strain CMS v-slfn (GenBank accession no. AAG37679), VACV-WR B2 (YP_233066) and B3 (YP_233067), and murine slfns m-slfn1 (AAH52869), m-slfn3 (NP_035539) and m-slfn8 (NP_853523). Protein sizes (number of aa) are shown on the right. (b) clustal w (Thompson et al., 1994) alignment of the m-slfn1, 3 and 8 conserved region with the C terminus of v-slfn. Identical residues are shown in black and residues conserved in two or three out of four sequences are shown in light or dark grey, respectively. Amino acid co-ordinates are indicated. (c) Unrooted phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of v-slfn from camelpox virus (CMLV), cowpox virus (CPXV), monkeypox virus (MPXV), ectromelia virus (ECTV), taterapox virus (GBLV) and m-slfns. Protein sequences were aligned using clustal w and an unrooted tree was generated based on this alignment using phylip on the European Bioinformatic Institute website (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/). Bootstrap values from 1000 replica samplings and the divergence scale (substitutions per site) are indicated.