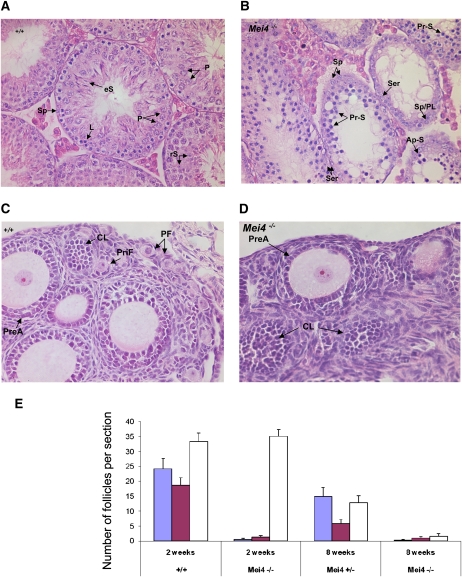
Figure 6.
Meiotic defects in testis and ovary from Mei4−/− mice. (A,B) Hematoxylin-eosin staining of testis from adult wild-type (A) and Mei4−/− (B) mice (n = 2 for each genotype). Among primary spermatocytes, some stages observed in wild-type testis were not present in Mei4−/− (i.e., pachynema, diplonema), whereas spermatocytes with apoptotic nuclei were frequent. Haploid cells (spermatids and spermatozoa) were never observed in Mei4−/−. (Sp) Spermatogonia; (eS) elongated spermatids; (rS) round spermatids; (P) pachynema; (Z) zygonema; (L) leptonema; (Ser) Sertoli; (Pr-S) primary spermatocyte at leptonema or zygonema; (PL) preleptonema; (Ap-S) apoptotic nuclei. (C,D) Hematoxylin-eosin staining of ovaries from 2-wk-old wild-type (C) or Mei4−/− (D) mice shows alteration in oogenesis. (PF) Primordial follicle; (CL) corpus luteum; (PreA) preantral oocyte; (PriF) primary follicle. (E) Quantification of primordial follicles (blue), primary follicles (purple), and growing follicles (white) in 2-wk-old (n = 3 for each genotype) and 8-wk-old (n = 1 for each genotype) wild-type, Mei4+/−, and Mei4−/− ovaries (error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals).