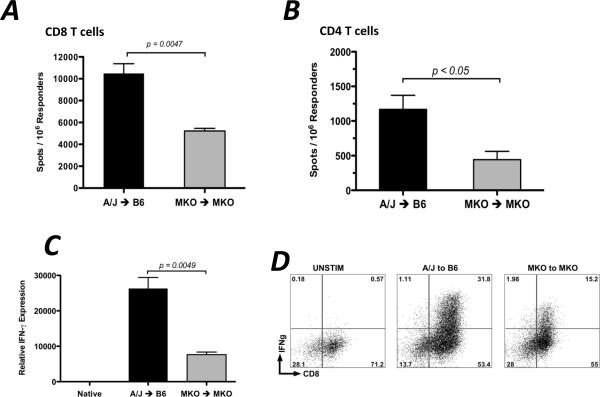
Figure 1. CXCL9 is required for maximum generation of donor-reactive, IFN-γ-producing CD8 T cells.
Wild-type or CXCL9−/− B6 mice received wild-type or CXCL9−/− A/J heart allografts. Recipient spleens were harvested on day 7 post-transplant and purified CD8 (A) or CD4 (B) T cells producing IFN-γ were enumerated by ELISPOT assay. Data is representative of at least 3 independent experiments. (C) mRNA was purified from total graft homogenates on day 7 post-transplant. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed on 5–6 samples/group. Expression of Mrpl32 was used as the endogenous control, and expression of IFN-γ in each sample was normalized to the expression in a random native heart sample. (D) Graft-infiltrating cells were purified on day 7 post-transplant and were re-stimulated in vitro with PMA/Ionomycin for 4 hr with monensin for the last 2 hr. Intracellular cytokine staining was performed using standard techniques and reagents. Numbers in each plot are percentages of total lymphocytes, and plots represent 4–5 samples per group. (E) Allografts were harvested at the times indicated and the number of graft-infiltrating CD8 T cells was quantitated using flow cytometry. Bars in each panel represent mean ± SEM; n = 5–6/group, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.