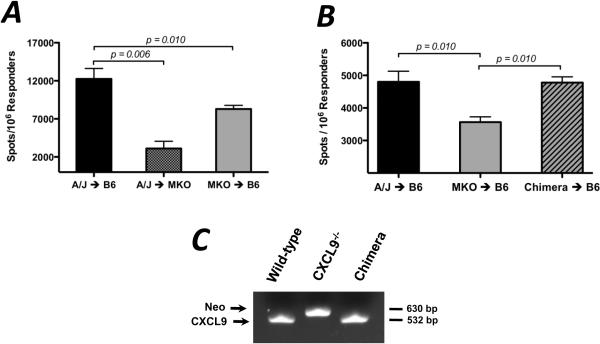
Figure 2. Donor- and recipient-derived CXCL9 influence the development of donor-reactive IFN-γ-producing CD8 T cells.
(A) Wild-type or CXCL9−/− B6 mice received wild-type or CXCL9−/− A/J heart allografts as shown. Recipient spleens were harvested on day 7 post-transplant and purified CD8 T cells producing IFN-γ were enumerated by ELISPOT assay. Data is representative of at least 3 independent experiments; n = 4–5/group, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (B) Chimerism of donor grafts in B was confirmed by PCR analysis of DNA from PBMCs collected from mice just prior to transplant. Data is representative of four mice per group. (C) CXCL9−/− A/J mice were irradiated and wild-type A/J bone marrow was adoptively transferred; mice were then rested for 8 weeks. These chimeric mice were then used as heart donors to wild-type B6 mice. CD8 T cells purified from recipient spleens on day 7 post-transplant, and IFN-γ-producing cells were enumerated using ELISPOT. Data is representative of 2 independent experiments; n = 3–4/group, ** p < 0.01.