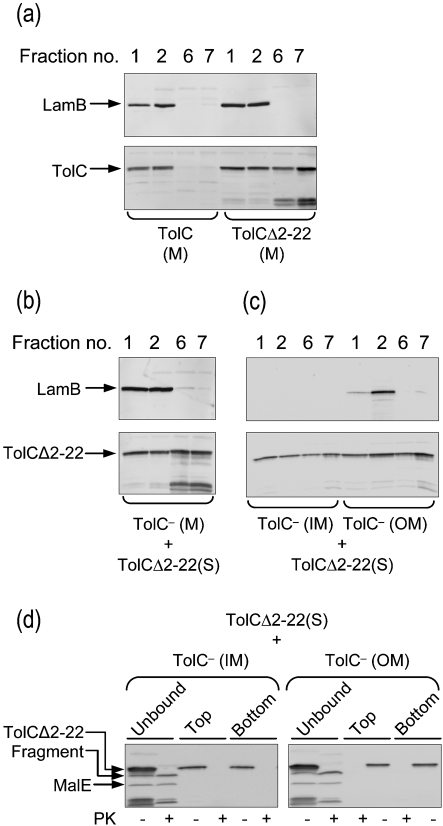
Fig. 2.
In vitro membrane association of TolCΔ2–22. (a) The membranes (M) from cells producing TolC or TolCΔ2–22 were separated from soluble proteins (S) and analysed by Histodenz density flotation gradients. Fractions were collected from top (1 and 2) to bottom (6 and 7) of the gradient. Note the presence of unknown TolC degradation products associated with the production of TolCΔ2–22. (b) Soluble TolCΔ2–22 was incubated with membranes obtained from RAM1330 (ΔtolC) and incubated for 1 h, after which the mixture was analysed by flotation gradient centrifugation. (c) Membranes of RAM1330 (ΔtolC) were separated into inner and outer membranes by sucrose density gradients. Fractions of equal volume of inner and outer membranes were mixed with the soluble fraction from cells producing TolCΔ2–22. After 1 h incubation at room temperature, the membranes were harvested by ultracentrifugation. Membrane-unbound proteins were withdrawn and membrane-bound proteins were subjected to flotation gradient centrifugation. (d) Proteinase K treatment of the membrane-unbound proteins and those in the top and bottom fractions from (c). LamB, TolCΔ2–22 and MalE were detected from various fractions by immunoblotting.