Fig. 5.
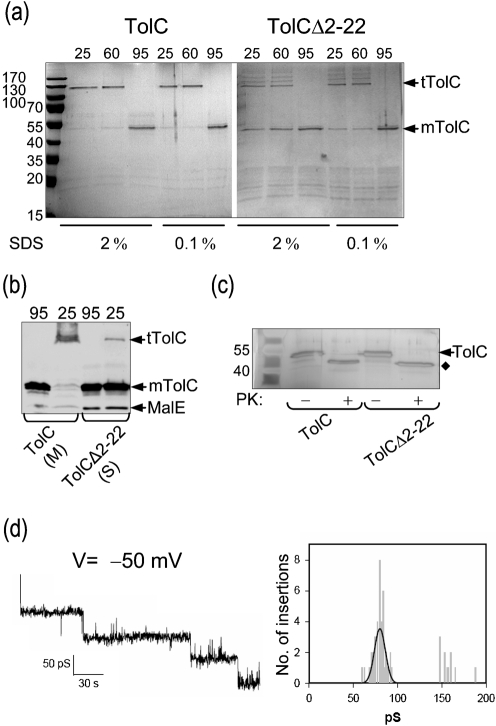
Purification of TolC and TolCΔ2–22 and electrophysiological analysis. (a) TolC was solubilized from membranes with 5 % Triton X-100. TolCΔ2–22 was recovered from the soluble protein fraction without any detergent. His-tagged TolC and TolCΔ2–22 were purified by immobilized-nickel affinity chromatography. A normalized sample from each elution peak was mixed with SDS loading buffer containing either 0.1 or 2 % SDS and heated at the indicated temperature prior to electrophoresis. Proteins were visualized by Coomassie blue staining; mTolC, monomers of TolC; tTolC, trimers of TolC. The migration of molecular mass standards is shown to the left. (b) Membrane (M) and soluble (S) fractions from the experiment described in Fig. 1(a) were mixed with loading buffer containing 2 % SDS and were unheated (25 °C) or heated (95 °C) for 10 min prior to electrophoresis. (c) The peak elution fractions were either untreated (−) or treated (+) with proteinase K. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining. (d) Channel-forming activity of purified TolCΔ2–22. Shown are sequential insertions and an associated amplitude histogram of purified TolCΔ2–22 in planar lipid bilayers at –50 mV in 1 M KCl.