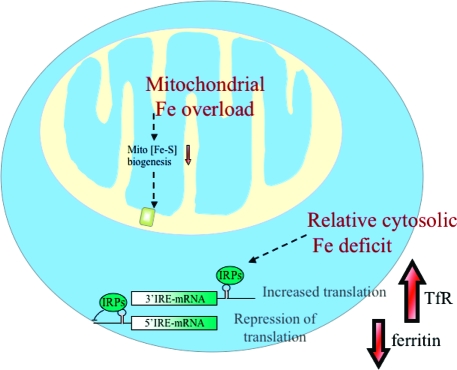
Figure 5.
Deficiency in mitochondrial Fe−S cluster biogenesis causes mitochondrial iron overload, relative cytosolic iron deficiency, and activation of the cytosolic iron sensor proteins, IRP1 and IRP2. Deficiency in many of the major proteins involved in mitochondrial Fe−S cluster biogenesis results in defective mitochondrial Fe−S cluster biogenesis, which in turn results in transcriptional remodeling, mitochondrial iron overload, and cytosolic iron deficiency. IRP proteins are activated to be RNA regulatory proteins, which increase the rate of translation of 3′ IRE-mRNA, such as TfR1, whereas they inhibit the translation of mRNAs that contain IREs in the 5′ UTR, such as ferritin and ferroportin.