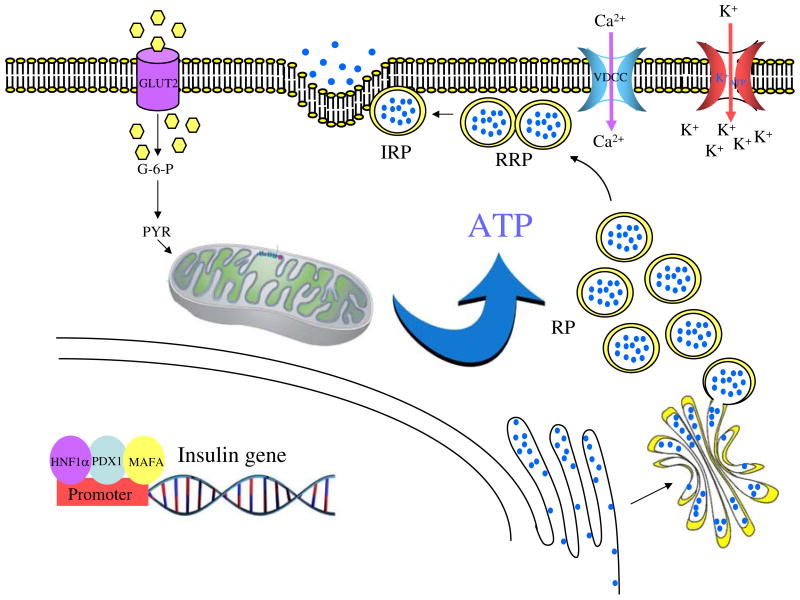
Fig. 1.
KATP-dependent GSIS. Insulin gene transcription is regulated by three transcription factors specific to the beta cell: HNF1α, PDX1 and MAFA [100]. An elevated level of extracellular glucose is taken up by GLUT2 before being rapidly phosphorylated to glucose-6 phosphate (G-6-P) by glucokinase. Pyruvate (PYR), the terminal product of glycolysis, is oxidised in the mitochondrion, yielding a large amount of ATP [101]. The increased cellular ATP:ADP ratio closes KATP-sensitive channels, resulting in membrane depolarisation, followed by Ca2+ influx through voltage-gate-dependent Ca2+ channels [5]. This drives the exocytosis of insulin granules. IRP, immediately releasable pool; RP, reserve pool; RRP, readily releasable pool; VDCC, voltage-gate-dependent calcium channel