Fig. 6.
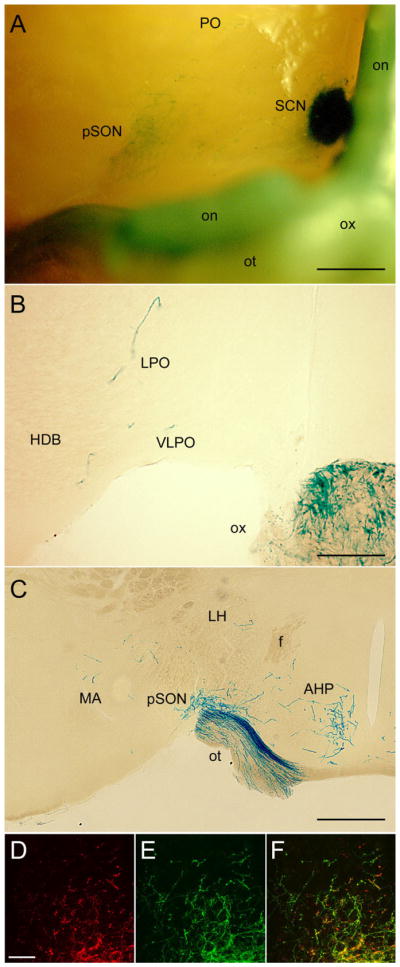
Hypothalamic and other basal limbic targets beyond the SCN. A: Basal view of X-gal-stained whole brain. Top of image is rostral and the right margin is near the midline. The optic chiasm and the right optic nerve and tract (left in image) have been retracted caudally to expose the right SCN and pSON. A few fibers are also evident in the preoptic region. B,C: X-gal staining in coronal sections just rostral (B) or caudal (C) to the SCN, showing scattered fibers in the preoptic area including the VLPO (B), dense input to the peri-SON (C), and scattered labeling in the anterior and lateral hypothalamus and medial amygdala (C). D–F: Confocal immunofluorescence images of the ventral SPZ illustrating relationship between crossed retinal afferents (red; D) and afferents from melanopsin RGCs (green, E). Format as in Figure 5C–E; F is the merged image. Many but not all of the crossed retinal afferents arise from β-galactosidase-positive (melanopsin) afferents. For abbreviations, see list. Scale bar = 500 μm in A and C; 200 μm in B; 25 μm in D (applies to D–F).
