Fig. 9.
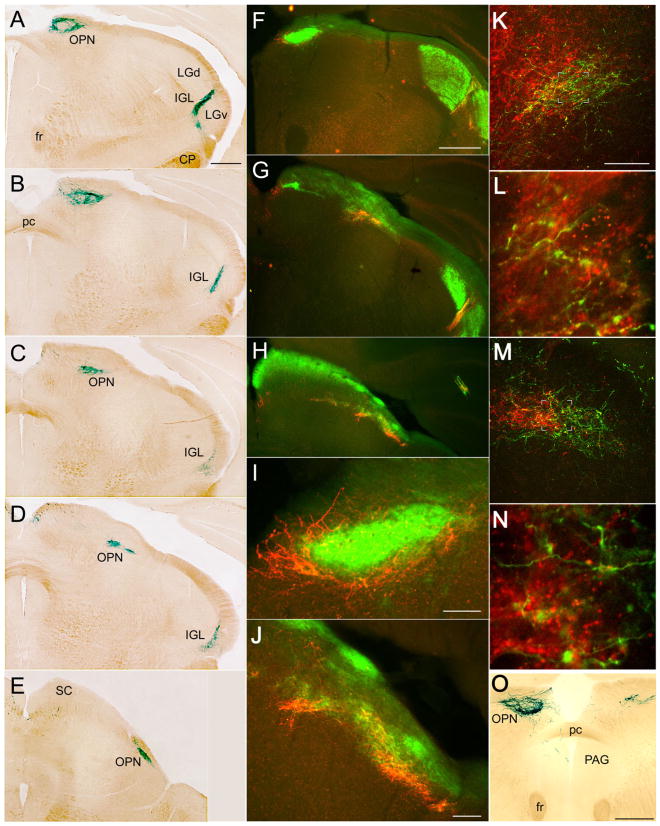
Distribution of afferents from melanopsin ganglion cells within the olivary pretectal nucleus (OPN), caudal IGL, and periaqueductal grey. A–E: Coronal series through the OPN stained with X-gal; section A is most rostral. F–J: Double-immunofluorescence micrographs of coronal sections illustrating relationship of afferents from melanopsin ganglion cells (red anti-β-galactosidase) with overall crossed retinal input (green CTB). F, G, and H are at roughly the same level as A, C, and D, respectively. I and J are higher power views of F and H, respectively. K,L: Confocal merged double-immunofluorescence images of the left OPN and adjacent pretectal nuclei illustrating the relationship between afferents from melanopsin RGCs (green; anti-β-galactosidase) and contralateral retinal afferents (red; anti-CTB; note that assignment of fluorophores is reversed from that in F–J). L is an enlarged, higher resolution scan of the boxed area in K. Note that the OPN, as defined by input from melanopsin afferents, is a small part of a much larger field of crossed retinal input (K). In L, most melanopsin afferents in the OPN contain anterograde label transported from the contralateral eye (green + red = yellow), but the terminal at the bottom right lacks red anti-CTB labeling and presumably arises from the ipsilateral eye. M,N: The same as K and L, but from the other side of the brain (right), so that anterograde CTB label (red) marks inputs from the ipsilateral eye. N is enlarged from the boxed region in M. In M, note the modest overlap between the field of melanopsin afferents (green) and the patch of uncrossed retinal input (red). Most melanopsin afferents in N lack anterograde label, presumably because they come from the contralateral eye. Within the OPN as defined by the melanopsin afferent terminal field, many retinal afferents, both crossed (K,L) and uncrossed (M,N), lack β-galactosidase (red +, green −) and thus presumably arise from non-melanopsin ganglion cells. O: Coronal section through the OPN stained with X-gal after enucleation of the left eye. Note the pronounced reduction in the labeled terminal field contralateral to the enucleation (right). On the left, fibers descending from the OPN penetrate the posterior commissure (pc) to enter the periaqueductal gray (PAG). For abbreviations, see list. Scale bar = 500 μm in A (applies to A–E), F (applies to F–H), and O; 200 μm in K (applies to K–M); 100 μm in I,J.