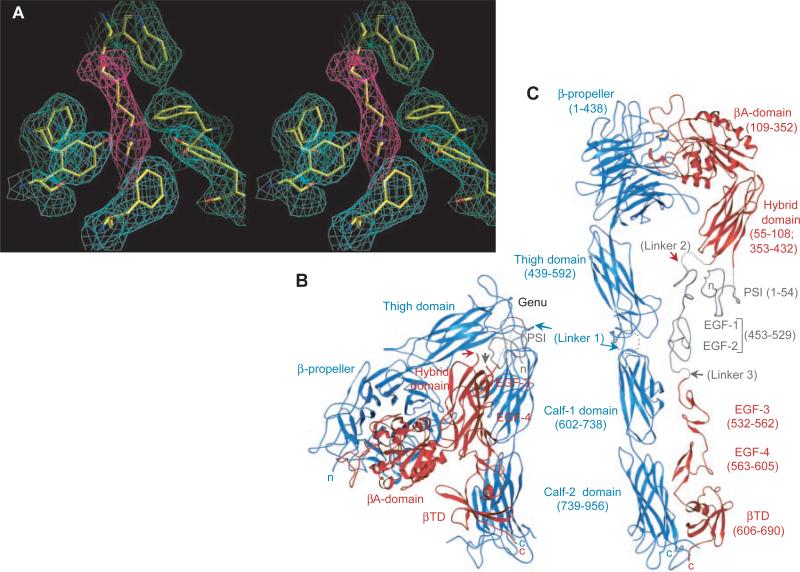
Fig. 1.
Structure of the extracellular segment of αVβ3. (A) Stereoview of a simulated-annealing omit map at 1.5 σ, in the vicinity of Arg261 (from β3) (magenta). Surrounding densities (cyan) (from α V) are from the same map. (B) Ribbon drawing (40) of crystallized αVβ3 [shown in blue (αV) and red (β3)]. (C) Model of the straightened extracellular segment of αVβ3. The two tails would extend into the plasma membrane in the native integrin. Translated and rotated EGF-3 and -4 show the approximate location of EGF-1 and -2 (gray). The PSI tracing (gray) is approximate. Connections of the untraced domains are in dotted lines. αV was straightened by extending the structure by 135° at the thigh–calf-1 interface (circled) and then rotating the calf module ~120° around its “long” axis to avoid clashes at the thigh–calf-1 interface. The same transformations were then applied to β3 (residue 445 onward). Arrows point to the position of the three longest inter-domain linkers 1, 2, and 3 in the structure. Amino acid domain boundaries are indicated in parenthesis. In this and other figures, “n” and “c” indicate NH2- and COOH-terminus, respectively.