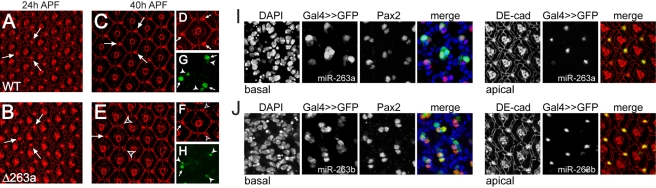
Figure 3. miR-263a inhibits apoptosis in the shaft cells.
(A–H) Projections of consecutive confocal sections of segments of pupal retinas. (A, C, D, G) Wild-type controls; (B, E, F, H) miR-263a mutants. (A, B) 24 h pupae; (C–H) 40 h pupae. (A–F) Anti-DE-cadherin staining (red). IOB are visible as large brightly labelled cells at alternating vertices of the ommatidial array (arrows). Open arrowheads in (E, F) indicate interommatidial vertices with missing shaft cells. (G, H) Pax2 (green) labels the nuclei of sheath cells (arrowheads) and shaft cells (arrows). The bristle cells have undergone several rounds of endoreplication and so have larger nuclei. The nuclei in (G, H) are located at different focal planes than the cell junctions in (D, F). (I, J) Projections of confocal sections of segments of pupal retinas at 30 h APF. Basal focal planes, left to right: DAPI labelled nuclei (blue in merged image); GFP whose expression was driven with miR-263a-Gal4 (I) or miR-263b-Gal4 (J) (green in merged image); Pax2 labelled IOB sheath (small nuclei) and bristle shaft cells (large nuclei; red in merged image). Apical focal planes of the same cells, left to right: cell outlines and IOB labelled with anti-DE-cadherin (red in merged image); miR-263a (I) and miR-263b (J) expressing cells visualized by GFP expression (green in merged image). Cell junctions (apical) are located at different focal planes than cell nuclei (basal).