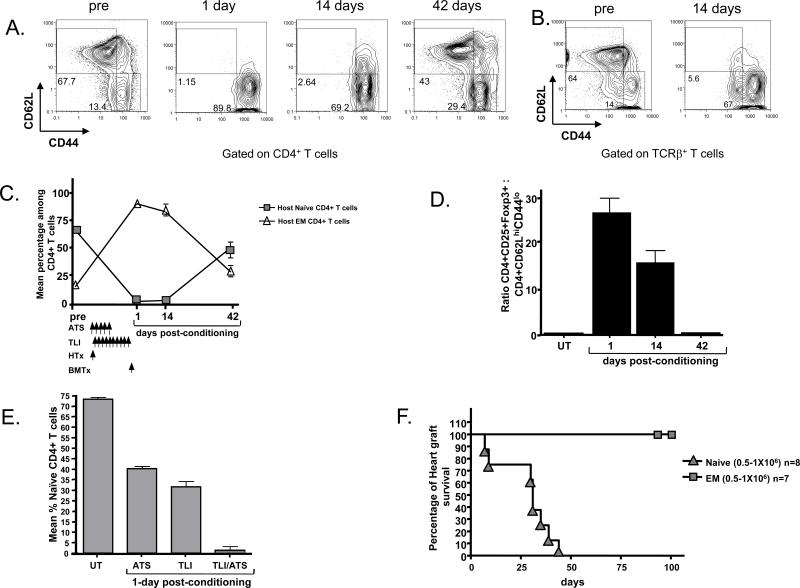
Figure 4. Reduced Proportion of Naïve T Cells in Transplant Recipients Further Alters the Balance of Effector and Regulatory T Cells.
A, representative FACS patterns of gated CD4+H-2Kd+ host type T cells for CD62L versus CD44 expression in wild type BALB/c mice before and 1 or 14 days after heart and bone marrow transplantation and TLI/ATS conditioning. Boxes show percentages of naïve (CD62L+CD44lo) and effector memory (CD62L-CD44hi) T cells. B, shows same analysis of gated host type total TCR+ T cells before and 14 days after transplantation. C, mean percentages of naïve and effector memory (EM) T cells among host CD4+ T cells before and after transplantation. N=6. D, mean ratios of host type CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ to CD4+ naïve T cells before and after transplantation. N=6. E, Mean percentages of naïve CD4+ T cells before and 5 days after conditioning with ATS alone, 24 hours after TLI alone, or 24 hours after TLI and ATS in combination without bone marrow or heart transplantation. Schedule of ATS and TLI administration was the same as in panel C. F, C57BL/6 heart graft survival in sublethally irradiated (300cGy TBI) RAG-2-/- BALB/c hosts after adoptive transfer of wild type BALB/c sorted naïve or effector memory phenotype T cells. Details of the sorting the latter cells have been described previously (31).