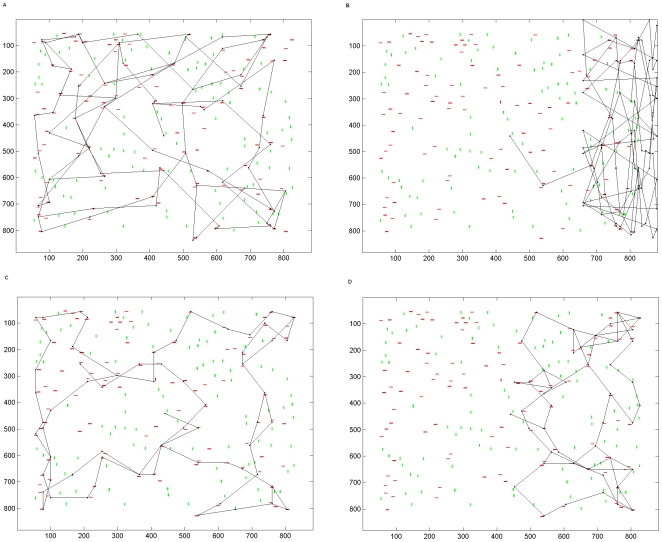
Figure 4. Simulated scan paths following parietal lesion.
a. A scan path obtained using the intact version of the model under overt attention. The target object is a red bar; hence most fixations land near red objects rather than near green objects or in blank regions of the scene. b. Scan path produced from overt attention when the parietal module is unilaterally lesioned. Severe symptoms of hemineglect are present in the scan path. This shows that visual hemineglect is produced when the parietal region that encodes stimuli in a retinotopic frame of reference is unilaterally lesioned and overt eye movements are made. This figure may be compared to the parietal patient behaviours shown in figure 1a and b. c. Attentional scanning movements produced by the intact model using covert attention. d. Symptoms of visual neglect in covert scanning produced when the model's parietal module was unilaterally lesioned. This shows that visual hemineglect is produced when the parietal region that encodes stimuli in a retinotopic frame of reference is unilaterally lesioned and covert attention is deployed. This figure may be compared to the parietal patient behaviours shown in figure 1a and b.