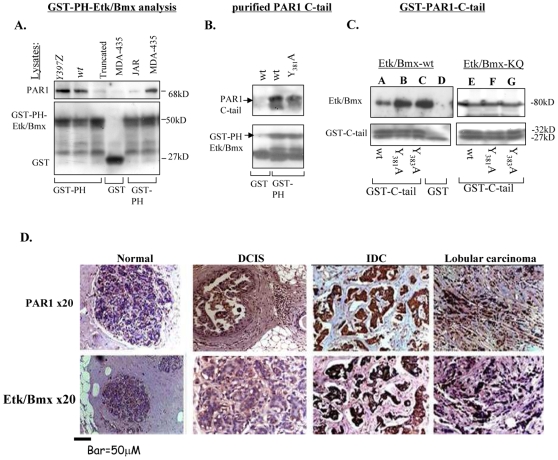
Figure 5. Physical association between PAR1 and Etk/Bmx.
A. PAR1 is physically associated with Etk-PH domain. Lysates of cells over-expressing Y397Z, wt or truncated hPar1, and lysates of cells that do not express PAR1 (e.g., JAR) were applied to a GST-Etk-PH column. Noticeably, highly metastatic MDA-435 cells express high levels of PAR1 Specifically-bound proteins were detected using anti- PAR1 antibodies. While Y397Z and wt hPar1 showed specific PAR1 association, lysates of the truncated hPar1 or JAR cells showed no binding. B. Purified PAR1 C-tail. PAR1 C-tail was cleaved from the immobilized GST-C-tail, purified and re-applied onto a GST-Etk-PH domain column. Specific binding is observed regardless of whether purified wt or mutant cleaved C-tail is analyzed. No binding was observed when only GST beads were used. C. GST- PAR1 C-tail of wt and mutants. Lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with either Etk/Bmx (A–D) or kinase-inactive Etk/Bmx (KQ; E–G), applied on various GST-PAR1-C-tail columns (PAR1-C-tail of wt, Y381A, Y383A) or GST-control column. The GST-C-tails from either wt hPar1 or mutants Y381A and Y383A are strongly associated with both wt (A–D) and kinase-inactive (KQ; E–G) Etk/Bmx. Control-free GST did not show any binding of KQ Etk/Bmx (data not shown). Specifically-bound proteins were identified using anti-Etk/Bmx antibodies. Levels of GST were used as a control for protein loading. D. Immunohistological staining of PAR1 and Etk/Bmx on breast tissue biopsy specimens. Antibodies directed against PAR1 (upper panel) or Etk/Bmx (lower panel) were applied to normal and cancerous breast tissue specimens. The cancerous tissues include DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ), IDC (invasive ductal carcinoma) and lobular invasive carcinoma (lobular carcinoma). The combined histological results were assessed and scored as outlined in the Materials and Methods section. The measurements per slide section was carried out using anatomical compartments, using an ocular micrometer (WHIOX2, Olympus, New Jersey, USA). The microscope was calibrated with a micrometer slide before each measurement. All measurements were performed on the monitor screen using a ×40 objective. On examining the sections for selection of fields tumor cells from the most cellular area at the center of the tumor were selected. Necrotic and inflammatory area were avoided. Eight microscopic fields were screened, 10 cells/field were selected and no less than 50 cells/tumor case were assessed. The positive rate of staining is expressed as a mean ± SD per tumor histological subtype from selected cases. Specific staining is observed in both PAR1 and Etk/Bmx, with particularly strong staining seen in IDC and lobular carcinoma. No staining is seen in the normal breast tissue. This staining represents total of 36 cases as outlined for each histological subtype in the table below, performed three times per category.