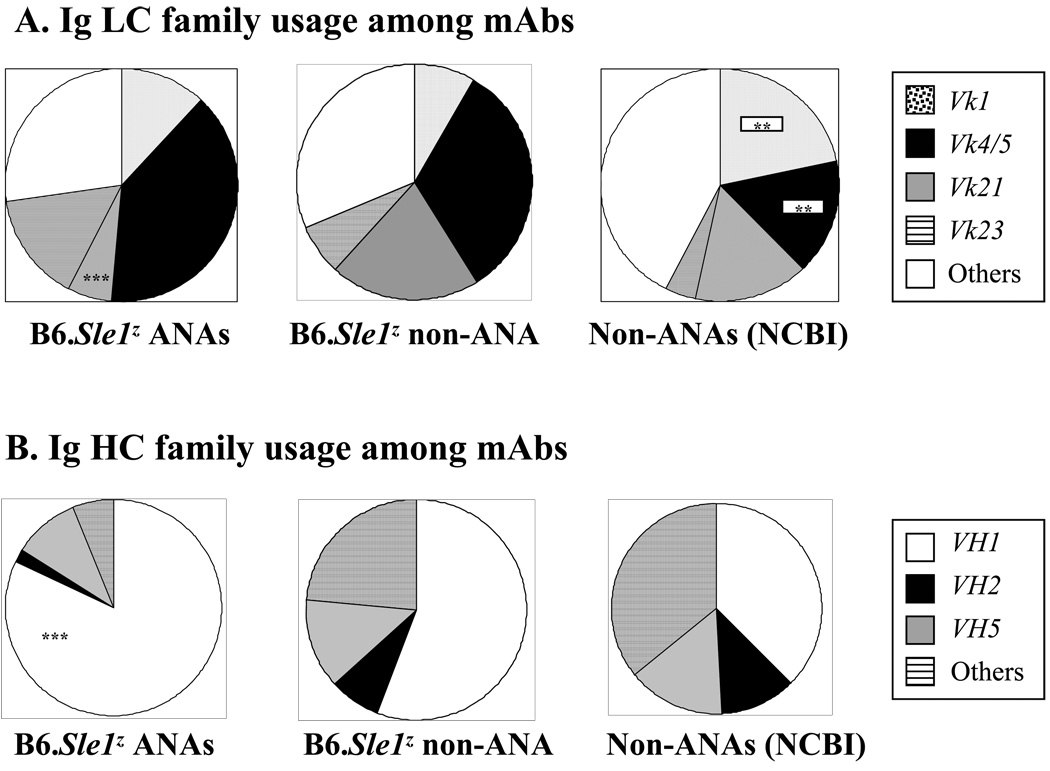
Figure 1. Ig HC and LC V-gene usage by the different groups of antibodies examined in this study A.
The Ig Vk LC gene family usage of B6.Sle1z-derived nuclear antigen reactive mAbs (as listed in Table 1) was compared to that of non-ANAs derived from the same strain or non-ANAs assembled from the NCBI/Genbank database, as described previously (Liang et al., 2003). In all 3 Ab groups, clonal replicates were represented by one member each; this resulted in a final panel of 32 ANAs, 73 non-ANA, and 145 non-ANA mAb LC sequences, respectively. Where ANAs differed significantly from B6.Sle1z non-ANAs (as determined using Chi squared test) this is indicated within the left-most pie; where the NCBI/Genbank-derived mAbs differed from the B6. Sle1z-derived mAbs, this is indicated in the right-most pie (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).
B. The Ig VH gene family usage of B6.Sle1z-derived nuclear antigen reactive mAbs (as listed in Table 1) was compared to that of non-ANAs derived from the same strain or non-ANAs assembled from the NCBI/Genbank database, as derived previously (Sedrak et al., 2003). In all 3 Ab groups, clonal replicates were represented by one member each; this resulted in a final panel of 32 ANAs, 58 non-ANAs and 165 non-ANA mAb HC sequences, respectively. Where ANAs differed significantly from the non-ANAs (as determined using Chi sequared test) this is indicated within the left-most pie (***, P < 0.001). No other differences reached statistical significance.