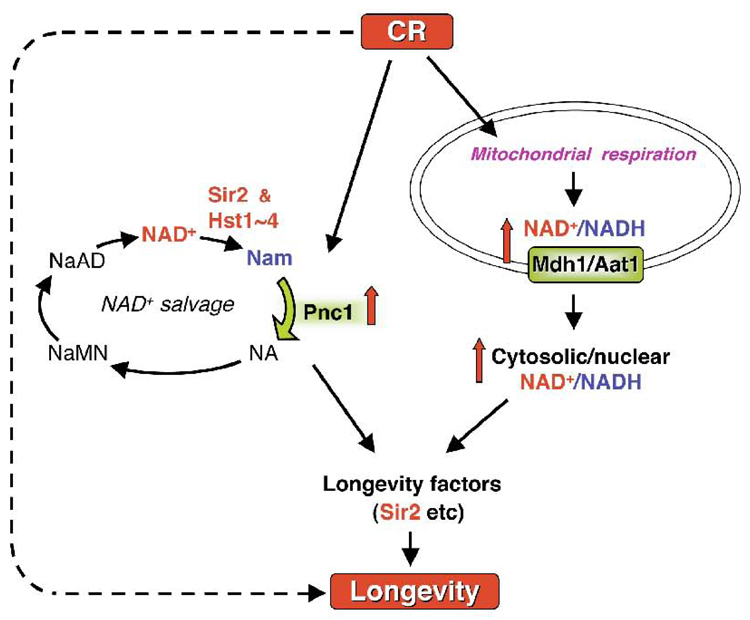
Fig. 2.
A model for CR-mediated life span extension in yeast. Multiple pathways mediate CR-induced life span extension. CR increases mitochondrial respiration and the concomitant elevation in NAD+/NADH ratio. The malate-aspartate NADH shuttle components (Mdh1/Aat1) function to balance redox equivalents between the mitochondrial and the cytosolic/nuclear pools, and are essential for relaying the metabolic signals in the mitochondria to downstream longevity factors, such as Sir2. CR also increases protein level of nicotinamidase Pnc1 in NAD+ salvage pathway. Up-regulation of Pnc1 facilitates the clearance of Nam and enhances Sir2 activity. Other Sir2-independent pathways also exist to mediate CR-induced beneficial effects including life span extension.