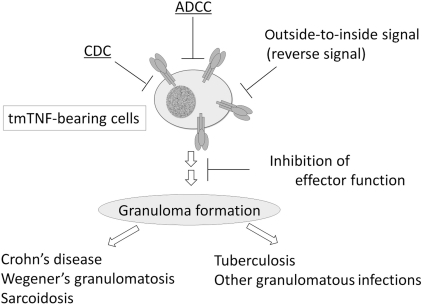
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of TNF-α-bearing cells by anti-TNF agents.
Transmembrane TNF-α plays an important role in granuloma formation, which is essential for the development of granulomatous diseases such as Crohn’s disease, and the host defence against tuberculosis. There are at least four distinct mechanisms for the inhibition of TNF-α-bearing cells by anti-TNF agents: (i) inhibition of transmembrane TNF-α-mediated effector function, (ii) destruction of TNF-α-bearing cells by CDC, (iii) destruction of TNF-α-bearing cells by ADCC and (iv) destruction of TNF-α-bearing cells by outside-to-inside signal (reverse signal).