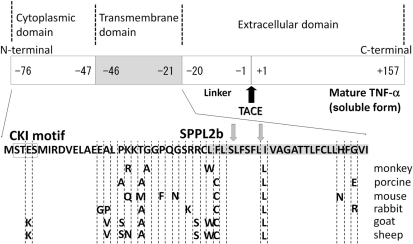
Fig. 6.
Structure of transmembrane TNF-α.
Transmembrane TNF-α is a type II polypeptide composed of a extracellular domain (177 amino acid residues), a transmembrane domain (26 amino acid residues, shaded) and an intracellular domain (30 amino acid residues). Mature TNF-α (soluble TNF-α) of 157 amino acid residues is cleaved from transmembrane TNF-α by TACE (black arrow). The remaining part is further cleaved by SPPL2b in the transmembrane domain (two grey arrows), and the intracellular domain is translocated into the nucleus to possibly modulate gene expression of the TNF-α-bearing cells. The intracellular domain contains CKI motif (boxed) and three serine residues. These serine residues are conserved among different species and are essential for the outside-to-inside signal transmitted by transmembrane TNF-α upon binding to anti-TNF antibody. Amino acid residues are shown in the one-letter code. The transmembrane domain of transmembrane TNF-α is shaded.