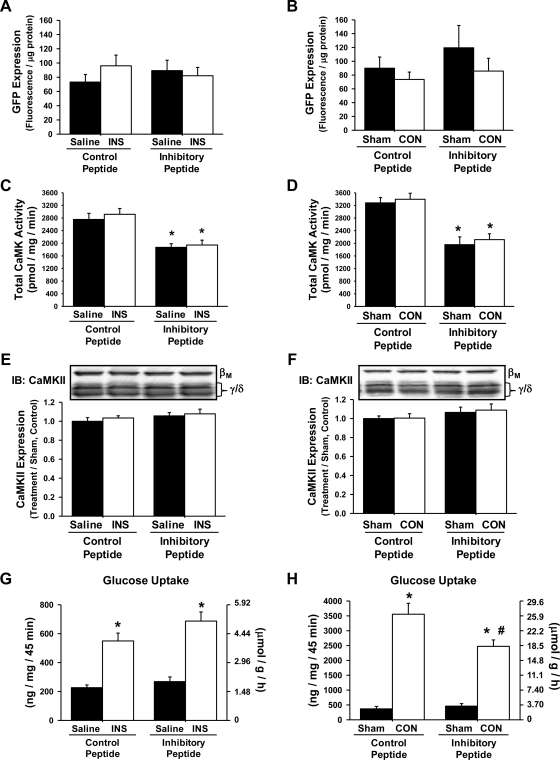
Fig. 4.
The green fluorescent protein (GFP)-CaMKII inhibitory peptide inhibits CON-induced but not insulin (INS)-induced glucose uptake into mouse tibialis anterior muscle. Mouse tibialis anterior muscles were transfected with expression vectors containing either the GFP-CaMKII inhibitory peptide or the GFP control peptide. After 1 wk, mice were anesthetized and then stimulated by CON or by injection of a glucose bolus to elicit a physiological INS response. Muscles were harvested to assess peptide expression, CaMK activity, CaMKII protein expression, and muscle 2-[3H]deoxyglucose uptake. A and B: peptide expression was assessed as fluorescence and was not significantly different among the treatment groups. C and D: total CaMK activity was assessed in muscles expressing the GFP inhibitory or GFP control peptide via [32P]ATP kinase assays. Expression of the inhibitory peptide decreased total muscle CaMK activity by ∼35% compared with the GFP control peptide muscles. E and F: CaMKII protein expression was not altered by expression of the GFP-CaMKII inhibitory peptide. G and H: INS-induced muscle glucose uptake was not affected by expression of the GFP-CaMKII inhibitory peptide, whereas CON-induced muscle glucose uptake was impaired ∼30%. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05. *Vs. saline or sham; #vs. control peptide (n = 6–14 muscles/group).