Fig. 1.
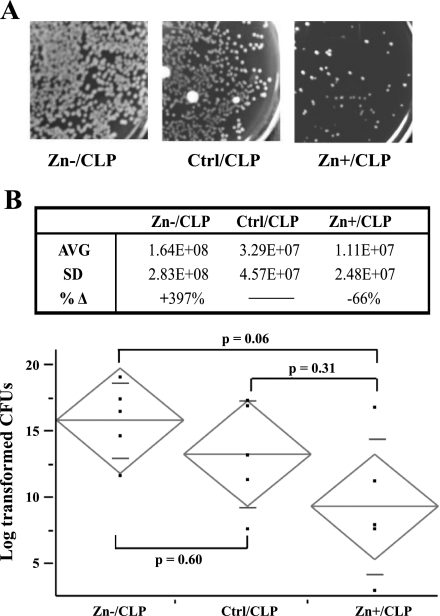
Zinc deficiency increases bacterial burden following cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Whole blood was obtained 24 h following CLP treatment, plated on blood agar following serial dilutions, and then incubated overnight and enumerated the following day. A: representative pictures of plates from the zinc-deficient (Zn−/CLP), zinc-sufficient (Ctrl/CLP), and zinc-supplemented (Zn+/CLP) treatment groups are shown. B, top: total bacterial counts were obtained from all animals in each treatment group. Average (AVG) and standard deviation (SD) are displayed in this table (n = 5 mice in each treatment group). %Δ Represents the % difference between the zinc-deficient (Zn−) or zinc-supplemented (Zn+) compared with the baseline control zinc diet (Ctrl). B, bottom: bacterial counts were log transformed to obtain a normal distribution and then displayed graphically (long horizontal line in the diamond = group mean, and short horizontal lines in the diamond = SD). The differences between all groups were assessed by ANOVA (P = 0.07) followed by the Tukey honestly significant difference test to look for trends between each group, P values are shown. No bacteria were present in animals placed on normal or zinc-modified diets (data not shown). This figure is representative of 2 separate experiments. cfu, Colony-forming units.