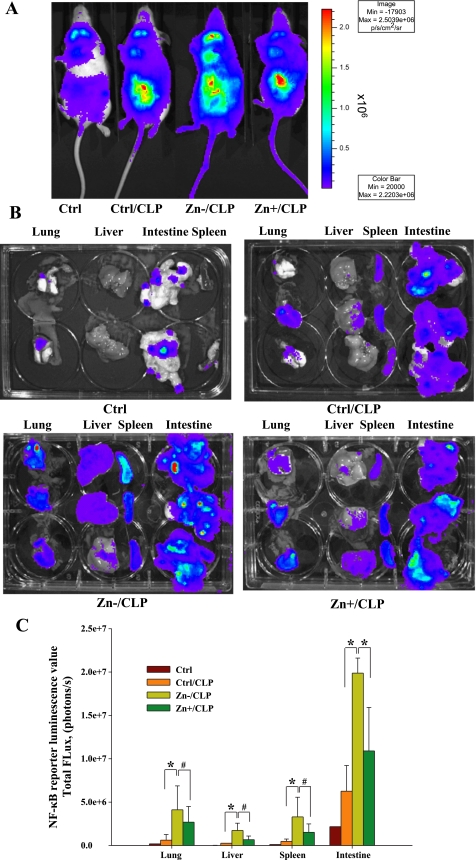
Fig. 2.
Zinc deficiency increases NF-κB activation systemically following CLP. A: a representative whole body image obtained from 1 mouse within each treatment group is shown and includes the untreated control diet (Ctrl) group along with analysis of mice 8 h after CLP in conjunction with 3 different zinc diets, including the control diet (Ctrl/CLP), a zinc-deficient diet (Zn−/CLP), or a zinc-deficient diet followed by acute zinc supplementation (Zn+/CLP) (n = 2 for untreated mice, n = 3 per dietary groups involving CLP treatment). The anesthetized mice were placed in a light-sealed chamber connected to the charge-coupled device (CCD) camera for image analysis. Luminescence emitted from each animal was integrated for 10 min starting 2 min after d-luciferin injection. B: vital organs including the liver, lung, spleen, and intestine were excised from each animal and immediately subjected to quantitative bioluminescent imaging. The composite images of each tissue from each animal are presented after color scale adjustment (the scale for A and B is identical). C: metric analysis of total photon flux of pooled data for each tissue from each treatment group (*P < 0.05, #not statistically significant).