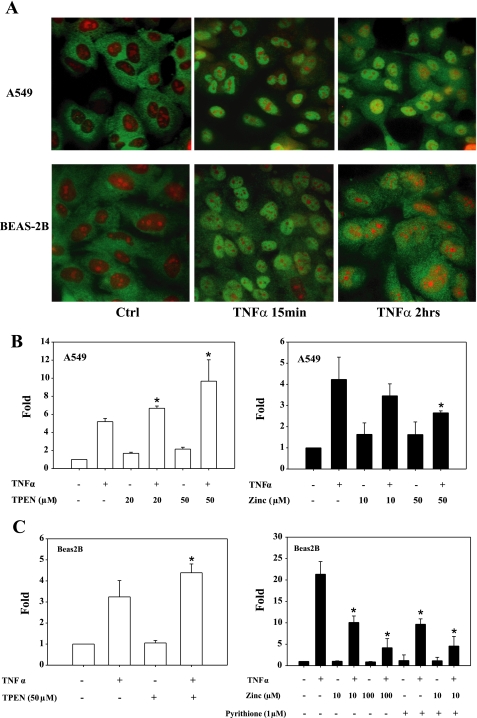
Fig. 7.
Zinc modulates NF-κB activity in human lung epithelia. A: TNFα (10 ng/ml) exposure lead to the rapid translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus of human lung epithelial cell lines A549 and BEAS-2B cells as determined by immunofluorescent detection of p65 protein (green). Propidium iodide was used to counterstain nuclei (red). B and C: zinc modulates NF-κB transactivation of a luciferase reporter gene (3×κB-luc) in A549 and BEAS-2B cells. Both cultures were transfected in triplicate with an NF-κB reporter plasmid (3×κB-luc). N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine (TPEN; 20 or 50 μM × 1 h) was then added to deplete intracellular zinc. Cells were then exposed to TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 6 h. Zinc inhibition study was done in combination with pyrithione before addition of TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 1 h (*P < 0.05 compared with the group of TNFα treatment only).