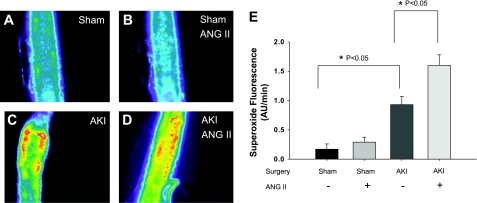
Fig. 1.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) induces alterations in superoxide levels in gracilis arteries (GA). Isolated GA were incubated with dihydroethidium (DHE) and evaluated via fluorescent microscopy. Representative fluorescent images were obtained from vessels derived from sham-operated rats (A and B) and post-AKI rats (C and D). Images were also evaluated prior to (A and C) and following (B and D) stimulation with ANG II (10−8 M). E: summarized data describing the rate of accumulation of superoxide fluorescence production in arbitrary units (AU) of fluorescent intensity per minute in the presence and absence of ANG II. *Significantly different vs. sham-operated or AKI controls (P < 0.05).